Articles in the Articles Category
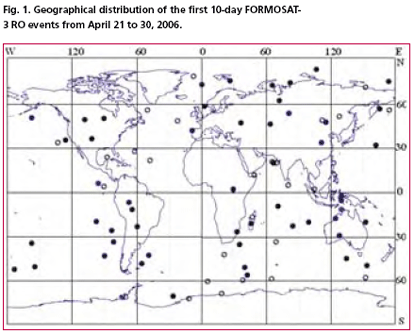
Six tiny FORMOSAT-3 satellites that were sped into space on April 15, 2006 are designed for systematic mass scale radio occultation (RO) studies of the Earth atmosphere and ionosphere at different altitudes by use of the GPS signals. Termed as the Formosa Satellite-3/ Constellation Observing System for Meteorology, Ionosphere, and Climate (FORMOSAT-3/COSMIC) mission, the new constellation’s primary science goal is to obtain in near real time the vertical profiles of temperature, pressure, refractivity, and water vapor in the neutral atmosphere, and the electron density in the ionosphere with global coverage. The measurements during five years of mission life will provide about 2,500 soundings per day, thus generating extensive information to support operational global weather prediction, climate change monitoring, ionospheric phenomena, and space weather research. The theory of RO measurements has been described previously (Gurvich and Krasilnikova, 1988; Yunck, 1988; Yakovlev, 2002; Hajj et al., 2002). During last four years, essential modernization in the RO technique has been introduced (e.g., Liou et al., 2002, 2006; Pavelyev et al., 2004 and references therein).
july 2006
GeoWeb 2006
24 – 28 July, Vancouver, BC, Canada
khenton@gita.org
2006 IEEE International Geoscience …
David Sharp was left to die.
Many saw him.
They didn’t do anything.
Perhaps they could not.
Perhaps it was ‘impossible’ to do …

With the launch of GPS in the 1980s, the task of providing control points for mapping purposes was greatly simplified, leading to economy and ease of operation. The technique of LASER mapping, which existed decades before GPS, also received a boost due to GPS, as instantaneous precise positioning of the exposure station during the mobile LASER mapping operation was made possible by GPS, thus solving a major problem in LASER mapping…
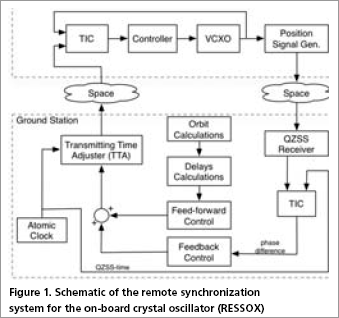
he Japanese Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS) represents an innovative multi-service satellite system able to provide positioning for mobile users over Eastern Asia and Australasia. The integration of the QZSS with the present GPS and the European GALILEO will improve accuracy, availability and capability over a wide area. Throughout a collaborative research program, the space technology group of AIST, Japan and the University of NSW…

Indonesian military plane to map quake-hit areas
The Indonesian Defence Forces (TNI) have assigned a CN-235 airplane to carry out aerial photography on areas in the Yogyakarta region affected by 27 May 5.9-magnitude earthquake. The activity is aimed at making a detailed map of areas devastated by the quake.
TNI had also sent a Hercules C-130 plane carrying a TNI field medical team and three helicopters to evacuate victims. http://news.xinhuanet.com
june 2006
International Conference in GIS and Health
27-29 June, Hong Kong
chankw1@hkuoc.hk
http;//geog.hku.hk/HealthGIS2006
July 2006
ISPRS …













 (5.00 out of 5)
(5.00 out of 5)