Articles in the Articles Category
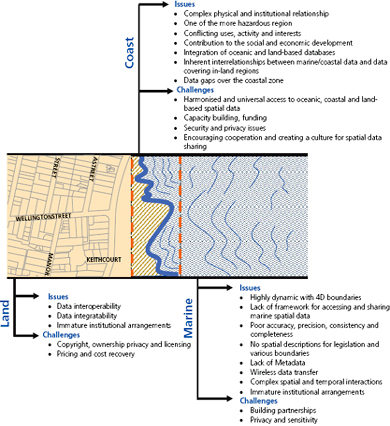
THE land-sea interface is one of the most complex areas of management in the world consisting of both the marine and terrestrial environments. The coastal zone is also home to an increasing number of activities, rights and interests. Population along the coastline is continuously increasing, bringing about new pressures on the fragile eco-system of the coastal zone. This has brought with it an increased need to more effectively and efficiently manage this area to meet the economic, environmental and social outcomes of sustainable development.
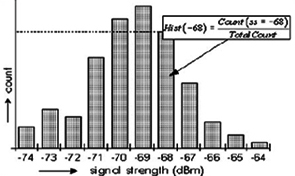
In particular the comfortable and mobile access to the internet were here the driving factors. Access points can nowadays be found in our daily environment, e.g. in many office buildings, public spaces and in urban areas. Parallel to this development there is meanwhile substantial interest in offering the user information which refers to the current location of the user (so-called Location Based Services LBS). Such Location Based Services, however, will be accepted by the user only if the cost performance ratio is satisfactory. If existing infrastructure such as WiFi without additional hardware installation can be used for location determination, then the realization costs are small and the service can be offered under attractive conditions. Several systems are nowadays available for location determination using WiFi signals. Their major application is the location determination of persons and objects inside buildings.

It is not just having computers in offices or creating websites, but it involves the creation of systems; integrating technology with administrative processes; human resources and dispensing information and services faster to the citizens. e-Governance offers a number of advantages for the government as well as the public. It shifts the centre of power from human agencies to technology, which is easier to deal with. For example, if a citizen wants some information on building codes, he/she has to go to the office of the local authority to get it, often shuttling from one table to another. If such information is made available on websites, it makes things easier for the citizens as well as the authorities.
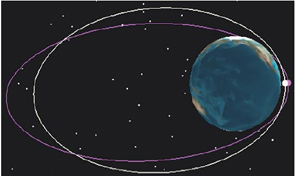
SVLBI (Space Very Long Baseline Interferometry) is an extension of the ground-based VLBI into the space. It has some important potential applications in geodesy and geodynamics, including the definition, practical realization, and the interconnection of different reference frames, determining the geocentric positions of VLBI stations, estimation of the gravity field of the Earth, and satellite orbit determination using the delay and delay rate observables.
It is not simply a project.
It is an ambition.
An assertion of technology.
And taking the technology beyond the realms of monopoly.
There are hurdles. Political and economical.
But stronger is the will to overcome them.
There are confl icts. On approach and interest.
There are frustrations on the delay. And, at stake is the credibility.
Still, there is a resolute to …
October 2007
36th Annual ILA Convention and Technical Symposium!
October 14-17, at the Embassy Suites Orlando International
Drive Orlando, Florida, USA
9th South-East Asian Survey Congress
28 October – 2 November,
Christchurch, New Zealand
http://www.conference.co.nz/ index.cfm/surveyors2007/The
Nav 07 Navigation Conference & Exhibition
30 Oct 2007 -01 Nov 2007
http://www.rin.org.uk
conference@rin.org.uk
27th INCA International Congress
Visakhapatnam, India
21-23 November 2007
www.hydrobharat.nic.in/Ist_Circular_INCA_2007.pdf
14th Session of the Asia-Paci?cRegional Space Agency Forum
21-23 November
Bangalore, India
www.aprsaf.org/text/ap14_info.html
ESRI …
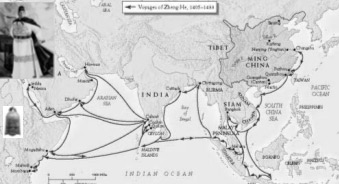
Zheng He’s Exploration of the Western Pacific Ocean and the Indian Ocean was an important event at the turning point of the world history. It was a golden opportunity for China to strengthen itself and make greater contributions to human beings. Unfortunately, to some extend, Zheng He’s magnificent feat in the history of navigation was later considered as a sheer waste of energy and money and a “failure policy”, and thus was put an end to. Zheng He’s trip, therefore, did not produce long-term effects. China still cut off itself from the out side world and stopped her exploration of ocean navigation, while Europeans, along the routes opened up by their expeditions, reached America, Africa and Asia and established colonies all over the world, which greatly promoted the capitalist development. In spite that the scale of Zheng He’s navigation far exceeded that of Columbus’s “Great Discovery” which followed some 80 years afterward, the former had much less effect on the progress of the world history.
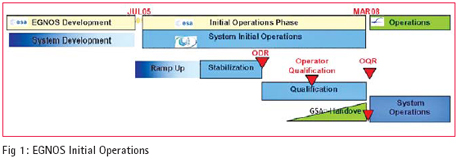
THIS paper describes of the activities performed by the European Satellite Services Provider (ESSP) and its partners in the establishment of the EGNOS system operations organization, the implementation and utilization of the operations processes and procedures and the operations products baseline as well as describing the management processes used within EGNOS operations with respect to preparation for Safety of Life Services.

ACCORDING to a recent Eurobarometer opinion survey, Europeans are highly positive about the GALILEO program, which aims to develop Europe’s own satellite-based navigation system. The survey indicates that most of EU citizens are aware of the role global positioning systems play in their everyday lives, know about possible applications and are firmly behind the development of such new technologies.
Furthermore, an overwhelming majority consider that Europe should set up an independent navigation system even if this involves securing additional public funds.
India celebrates 60 years of independence.
We are happy once again.
A celebration for democracy and democratic values.
On the occasion, we take a look at two movements.
National Spatial Data Infrastructure and Sustainable …










 (5.00 out of 5)
(5.00 out of 5)