To carry out the infrastructural development in any area, topographical maps (accurate, reliable and updated) of that area are of vital important. Topographic maps are also important aids for administrative and strategic planning, disaster mitigation, socioeconomic development and other related activities. In order to prepare topographic map, it is prerequisite to have grid coordinates as well as elevations of control points.

Space borne Remote Sensing technology has proved to be an important tool in rapid assessment and mapping of natural resources over a large area with reasonable accuracy. Application of satellite data in assessment of forest cover in India was first demonstrated by the National Remote Sensing Agency (NRSA), Department of Space, Hyderabad in 1985 when it came out with first ever estimate of country’s forest cover based on interpretation of Landsat (an American Satellite) data. Almost simultaneously, Forest Survey of India (FSI), Ministry of Environment & Forests started interpretation of satellite data for assessment of forest cover of the country and published country’s forest cover in 1987 using Landsat (MSS) data, the most reliable data at the time.
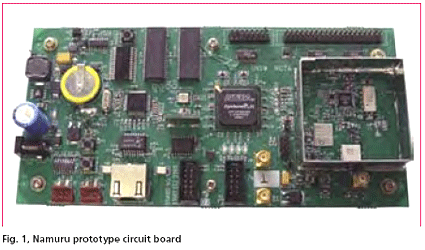
Development of a Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) based GNSS receiver platform has been underway at the University of New South Wales (UNSW) ‘SNAP’ lab since 2004. The receiver now has a name; ‘Namuru’ that means ‘to see the way’ in the language of the Eora people who inhabited an area around Sydney, including the UNSW campus, before the arrival of the British. The receiver was introduced in the Coordinates January 2006 edition and in this article we first provide a brief recap and then look at the latest developments and results from testing. But before launching into this, the question of why such a research and development platform is desirable must be answered.
EU and the Republic of Korea seal their agreement
During the EU/South Korea summit held in Helsinki, the two parties formally signed an agreement on cooperation on the European satellite radio navigation programme GALILEO. The agreement provides for numerous areas of co-operation, including cooperative activities in the areas of scientific research and training, industrial cooperation, trade and market development, standards, certification and regulatory measures. http://europa.eu.int

Innovative battlefield learning experience for soldiers
The Singapore Armed Forces (SAF) has introduced an innovative training and learning system for its soldiers called Battlefield Instrumentation (BFI). Utilising modern laser and informationcommunication technologies, BFI System brings together soldiers, weapon systems and fighting platforms. It uses the GPS, computer simulation and data communication to record details of battlefield engagements between opposing forces. www.channelnewsasia.com













 (5.00 out of 5)
(5.00 out of 5)