
Geospatial data to go online with Brunei Spatial Data Infrastructure launch
BSDI is the technology, standards, access system and protocols necessary to harmonise all of the Sultanate’s geospatial databases and make them available on the internet. It is facilitated by the Ministry of Development and led by the Department of Survey in partnership with the Land and Town and Country Planning. BSDI will publish base layers of geographic data such as elevations, transportation systems and water bodies that provide context and reference information for Brunei Darussalam. http://www.brunei-online.com

More than 100 million users of mobile LBS in Europe by 2012
According to Berg Insight, more than 100 million mobile subscribers in Europe will use LBS by 2012. Mapping, navigation and search are believed to become the top applications, followed by social networking and tracking. johan.fagerberg@berginsight.com
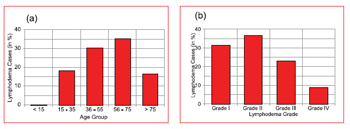
The disability problem due to Lmphatic Filariasis (LF) disease has been reported in 80 countries Ottesan EA (2000). Globally, the 1.1 billion people are exposed to risk of LF and the estimated LF affected population is 120 million Ottesan EA (2000), Michael E et al. (1996). Our recent estimation showed that there are 21 million diseased individuals in India alone Sabesan S et al. (2000) contributing approximately 40 per cent of global burden. A progressive lymphadema with increasing episodic attack adenolymphngistis (ADL) is the most important cause of physical suffering, permanent disability Pani SP and Lall R (1998) and the economic loss of the affected individuals and the community Ramaiah KD et al. (1998, 1999, 2000). Apart from these LF is also responsible for social problems including sexual disability and discomfort of marital life Dreyer G et al (1997).
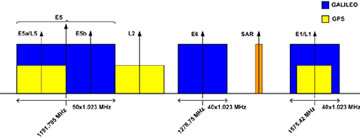
E5 band (1164 -1215 MHz), composed of E5a and E5b bands, is part of the spectrum allocated by ITU for new Radio Navigation Satellite Services in 2000. E5 signal has the wider bandwidth (51.150 MHz) never used in satellite navigation. Galileo E5 signal is composed by two data components and two pilot components broadcasted together by means of the multiplexing scheme AltBOC(15,10). E5a band will be used for Freely/NAV message (Open Service) and the codes of data and pilot components are uncripted, E5b band will be used for Integrity/NAV message for Safety of Life and Open Service. Integrity of signal is probably the most advanced service introduced by Galileo [1]. One of the main feature of E5 band is that the signal can be received in two ways: the first is to filter and demodulate only one of side bands E5a or E5b (see Fig. 1) the second is to process the overall received signal containing the components of both bands [2],[3]. In this sections is considered the second way because it will be adopted by professional receivers and this will avoid to obtain all the advantages of Galileo signal. E5 is the most promising signal in terms of performance in multipath environment and positioning for critical applications but also the most challenging for a receiver or a simulation. In this paper will be presented the simulation of the transmission and reception of E5 signal. It will be first described the generation of codes, then it will be illustrated Galileo AltBOC(15,10) signal structure and its differences with a conventional AltBOC, it will be shown a way for the generation of that signal and some basic characteristics for the development of a software receiver for E5.

Spirent delivers 3 carrier solution, launches GSS8000
The architecture of Spirent’s systems is designed to support coherent simulation of multiple GNSS signals together. The SimGEN for Windows® software enables control and flexibility over multiple satellite constellations as well as interference sources and augmentation systems such as EGNOS and WAAS. It operates in real time to generate simulated RF signals across all GNSS and interference signals. Spirent Communications has also recently launched new Spirent GSS8000 simulation system, a signal generator unit for GPS, Galileo and GLONASS testing. It tests advanced satellite navigation technologies and offers enhanced capability, increased flexibility and improved signal fidelity.This new solution supports processing rates as low as 4 ms with pseudorange accuracy at 1 mm for many scenarios. Its new design allows for a wide variety of configurations from GPS L1 right up to comprehensive multi-RF output and/or multi-constellation test systems. http://www.spirent.com

As per the textbook theory of market maturity in any country, the expected stages are that of market development, rapid growth, saturation or maturity and the decline. Having had the good fortune to predict the evolution of GPS Navigation market in India, here is a retrospective of the various phases, from both the vendor’s and consumer perspective.
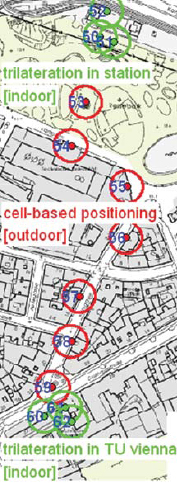
Alternative location methods for absolute positioning in areas where no GNSS position determination is possible due to obstruction of the satellite signals are needed in mobile positioning. Active RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) can be used also for position determination, although the system was not only developed for positioning and tracking but mainly for identification of objects. Using RFID in positioning, different approaches can be distinguished, i.e., cell-based positioning if the RFID tags are installed at active landmarks (i.e., known locations) in the surroundings, trilateration if ranges to the RFID tags are deducted from received signal strength (RSS in RFID terms) values and location fingerprinting where the measured signal power levels are used directly to obtain a position fix. Using Cell of Origin (CoO) the achievable positioning accuracy depends on the size of the cell and is therefore usually several metres up to 10’s of metres using long range RFID equipment. Higher positioning accuracies can be obtained using trilateration and fingerprinting. In this paper the use of trilateration is investigated.
May 2008
International Conference: “Studying, Modelingand Sense Making of Planet Earth
1 – 6 June, 2008
Department of Geography, University of the Aegean, Mytilene, Lesvos , Greece
http://www.aegean.gr/geography/earthconference2008/en/main_fr.htm
Navigation and Location Europe 2008
4 – 5 …

The potential of cell-based positioning for improving LBS
Markus Ray
Active RFID trilateration for indoor positioning
Guenther Retscher, Qing Fu
Evolution of GPS Navigation in India
Amit Prasad
Simulation of Galileo E5 Signal
Fantinato Samuele
GIS for lymphatic filariasis morbidity management and control
M Palaniyandi










 (5.00 out of 5)
(5.00 out of 5)