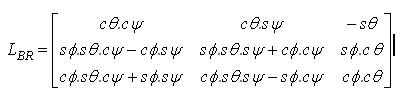
For the final evaluation of a GPS attitude determination algorithm (GADA), it was determined its true performance in terms of its accuracy, reliability and dynamic response. To accomplish that, a flight test campaign was carried out at the Brazilian Flight Test Division (GEEV) to validate the attitude determination algorithm. In this phase, the measured aircraft attitude was compared to a reference attitude, to allow the determination of the errors…

Geolocation to the web
Opera Software and Skyhook Wireless to partner in bringing geolocation to the Web. With Skyhook’s Wi-Fi Positioning System (WPS), any computer or mobile phone with a wireless adapter can take advantage of its positioning technology and locate a user. Users
can now simply choose to share their location with any Web site and get a range of information. www.opera.com
May 2009
ENC-GNSS 2009
3-6 May
Naples, Italy
www.enc.gnss09.it
International Conference on Integrated Navigation Systems
25-27 May
Saint Petersburg, Russia
http://www.elektropribor.spb.ru
EOGC2009
25-29 May
Chengdu,China
http://www.eogc2009.com.cn
June 2009
GSDI 11 World Conference
Rotterdam, The Netherlands
http://gsdi.org/gsd11
TRANS-NAV 2009
8th …

Mission Possible
It is a seamless backup to GPS. {Paragraph} {Also please check there must be good enough line spacing}
It is cost-effective and completely interoperable.
Asserts The Independent Assessment Team (IAT).
Also, recommends unanimously to US Government.
To complete the eLoran upgrade and commit it as the national backup to GPS.
Two …

The GNSS Research and Application Centre of Excellence (GRACE), is a cross disciplinary centre providing cutting edge research, high calibre teaching, and business support services to the GNSS community. In October 2009 GRACE will move into its own state-of-the-art purpose built centre. A ground breaking ceremony took place on the 11th of November 2008, and construction of the centre is underway at the University of Nottingham Innovation Park (UNIP) on the Jubilee campus of the University of Nottingham.
It will be the only facility in UK dedicated to the development of downstream applications and services using GNSS. The European Union has estimated the market for downstream applications and services to be worth in excess of £230 billion by the year 2025. Supporting the University of Nottingham in this venture which will have an investment of £9.2m is the East Midlands Development Agency (EMDA), one of the nine regional development agencies in England. EMDA was established in 1999 with the primary goal to increase the economic growth of the East Midlands region.

Adding GRACE to GNSS
National Land Records Modernisation Programme: Misson Possible
Flight Evaluation of a GPS Attitude Determination Algorithm
Dr Nelson Paiva Oliveira Leite and Prof Dr
Fernand o Walter
A sensor architecture for high precision UAS navigation
Luca Garbarino, Vittorio Di Vito, Ettore De Lellis, Carmine Marrone, Federico Corraro

Norway joins Galileo project
The Norwegian government will give a boost by providing 68.9 million euros (92.5 million dollars) towards the 3.4 billion euro project. While Norway is not a member of the 27-member bloc, the
country’s economy and business minister Sylvia Brustad said it was important that Oslo took part in Galileo’s development. “The project will be of huge importance for the development of the European space industry and it is therefore important that Norwegian businesses are now able to compete,” Brustad said in a statement. In
September, the European Commission and the European Space Agency, which includes Norway as a member, shortlisted 11 European firms which are bidding for future contracts connected to Galileo. www.newsabout- space.org/story/157986254.html

On August 21, 2008 the cabinet approved the proposal of the Department of Land Resources (DoLR), Ministry of Rural Development to merge two existing centrally sponsored schemes and replace them with the modifi ed scheme of National Land Records Modernization Program (NLRMP). The two schemes being merged are the Strengthening of Revenue Administration & Updating of Land Records (SRA&ULR) and Computerization of Land Records (CLR).










 (5.00 out of 5)
(5.00 out of 5)