Articles in the Articles Category
Prof Madhav N Kulakrni.
A member of Coordinates family.
We had been fortunate to have his guidance for last two years.
His sudden demise has left us in shock.
His name itself was synonym of GPS/Geodesy in India.
An irreparable loss to GPS community and science.
We share our heartfelt grief with the bereaved family and pray for strength to …
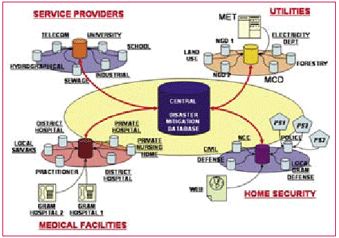
In recent past , humanity has suffered an increasing number of natural disasters affecting more than 2.5billion people, killing 478,100 and causing economic losses of about US$690bn (UNEP/ GRID-Arendal, 2005). Some of the distinctive instances are: December 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and its concomitant tsunamis, The US eastern coast and Central America, hurricanes Katrina, Rita, Mitch, Stan and Wilma in September-October 2005, Pakistani earthquake of 2005, and now the current avian influenza in Asia and Europe. Natural and manmade tragedies, such as earthquakes, foods, nuclear catastrophes, pose an ever-present challenge to emergency services. Victims and societies at large have responded differently in each case. Some were heroic, some responsible but many panicked and responded irrationally. This aggravated the already bad situation. All of them could have responded more effectively if they were better informed and aright managed.

Exact determination of position, at any time, from any location, secure and precise navigation, efficient route planning – in the future it will all be summed up in one word: Galileo. This new European navigation system with 30 satellites will be ready for use in the beginning of the next decade. A first test satellite has been launched into its orbit in 2005. Another one will follow by the end of this year. Galileo will make civil users of satellite navigation in Europe and all over the world independent of the American Global Positioning System (GPS). Even more, especially in connection with civilian use, Galileo will outperform GPS and thereby open the gate for new applications and markets for satellite supported navigation. Especially in the combination with navigation, mobile telecommunication and information services, there is an immense utilisation and market potential.

Fifteen years ago people hardly had mobile phones; today it seems awkward if you do not possess one. After this success story the IT sector has its new gadget: Navigation systems. Similar to the mobile phone market it is growing tremendously.
Market structure
That fierce competition has served well to bring prices down. So, nowadays most players are sourcing their products from sub-manufacturers in China. However, this means that anybody can enter the market and source easily navigation devices, when the volume commitment is big enough.

Tsunami is a series of traveling waves of extremely long wavelength generated primarily by earthquake occurring below and near the ocean floor. Underwater volcanic eruptions and landslides can also generate tsunami. Though the return period of tsunami is infrequent, the destruction done by tsunami is widespread, in terms of life and property. The most devastating tsunami occurred in December, 2004 affected the coastal countries of the entire Indian Ocean. It became necessary to set up a system in India to monitor seismic activity and sea level to evaluate potentially tsunamigenic waves and disseminate tsunami alert or warning.

With the continued growth of urban centers all around the world, city planners are required to keep up with up-to-date geographical at a faster rate. This has led to the establishment of spatially-referenced Geographic Information Systems (GIS) for a variety of municipal applications. This information, however, is expensive to obtain by conventional methods. In addition, conventional methods supply only point solutions and are therefore not suited to support the increasingly complex requirements posed by urban centers in a timely fashion. Satellite remote sensing and aerial photogrammetry are two methods which can provide various GIS information at high rates and reasonable cost. However, with the first method, the associated accuracy is not suitable for many applications, and in the second case the near vertical field of view provides only part of the information required.
May 2007
International Conference on Integrated Navigation System
28-30 May, Saint Petersburg,
Russia elprib-onti@telros.net
Geoinformation for Disaster Management (Gi4DM2007)
23-25 May, Toronto, Canada
junli@ryerson.ca
5th International Symposium on Mobile Mapping Technology
28-31 May, Padova, Italy
naser@geomatics.ucalgary.ca
June 2007
Navigation Europe 2007
6-7 June 2007 in Amsterdam.
www.telematicsupdate.com/naveurope2007/
21st Pacific Science Congress
12-16 June, Okinawa, Japan
psc21@to.jim.u-ryukyu.ac.jp.
Spatial Data Quality 2007 5th International Symposium
13-15 June, ITC, Enschede,
The Netherlands
issdq2007@itc.nl
27th …

Sunderban, one of the largest mangrove forests in the world, is located in the deltaic region of Ganga and Bramhaputra rivers in India and Bangladesh. The impact of biotic and abiotic factors on Sunderban is enormous (Rao, 1959), due to which the area has got reduced to nearly half during the past few centuries (Blasco, 1975; Naskar and Guha Bakshi, 1982; Naskar, 1985).
The mangrove-forested area of Sunderban (including portions in Bangladesh) was recorded to be 20,000 km2 by Clark (Annon., 1895), and 17,500 km2 by Prain in 1903. Grif?th (1982) reported that mangrove forests in the Sunderban covered over 4264 km2 and 4109 km2 respectively in India and Bangladesh during early eighties. The present area of Sunderban is 2081 km2 (Anon., 2001).
The debate is intense.
So are interests, and the clash of interests.
Conflicts are visible.
Equally visible is the cynicism displayed by some.
We could see all these forces at play in the Munich
Satellite Navigation Summit last month.
Still, there is a hope.
There is also a strong sense of conviction, commitment and confidence.
Galileo will happen.
It has to.
It is just a …

The onset of the 21st century marked the beginning of the Asia-Paci?c era. This is the region where most of the world’s growth and economic development will occur over the next twenty years. The new millennium also signaled the birth of the urban era. Half of the world’s population now lives in cities, and that number is growing rapidly. In fact, the rate of urbanization in the Asia/Paci?c is alarming. The region currently has a population of 3.5 billion people; with that number expect to grow to 5 billion within the next 20 years. Most of that growth will occur in Asia’s cities.
This rapid urbanization presents staggering challenges for the region’s city governments. Up until now, most cities have not developed in a sustainable way. Economic development, land use planning, urban infrastructure, sewers, potable water systems, solid waste handling, and transportation systems are all inadequate to meet current needs let alone the rapid growth that lie ahead.









 (5.00 out of 5)
(5.00 out of 5)