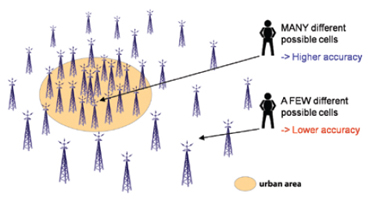
Most of today’s Location Based Services (LBS) provide information based solely on a users’ location, not taking into account context knowledge about the user’s current situation and needs. This often results in low-quality and inappropriate information to the user. Hence, in order to provide user-oriented services, an improvement of the response-quality of information requests is required. Knowledge about the coordinates of places where the user regularly stays in her life combined with semantics about such places can provide valuable knowledge for LBS. Zhou et al.

Taiwan’s GPS makers to tap European market with new devices
According to industry sources, Taiwanese GPS devices makers like Mio Technology Ltd. and Asustek Computer Inc are actively tapping the European market this year, with new products. Global sales of GPS devices are estimated to top US$30 billion this year. Europe absorbs nearly 60% of world`s total annual shipment. Last year, sales in the European market sharply shot up 82%. http://cens.com//cens/

Nokia launches global Ad campaign for GPS-enabled N82 handset
“The Urbanista Diaries,” is the new global campaign by Nokia to promote the recently launched Nokia N82 that features a 5 megapixel camera and integrated GPS. The campaign engages bloggers, journalists, and everyday people to promote the phone.

3D-Laser Scanning possible up to 2000m
RIEGL has recently launched 3D laser scanner LMS-Z620, especially optimised for long range topography and mining applications. It is providing a maximum measurement range of 2000m on natural targets and a reduced beam divergence of just 0.15 mrad, performance data which are unrivalled in the market of high-speed laser scanners. It has RiSCAN PRO´s backsighting and Multi Station Adjustment functionality as well. www.riegl.com

Special characteristic of spatial data is that it can be shared and used for many other purposes than the one, for which, it was originally produced. To facilitate its efficient sharing and reuse, it needs to be properly managed in the form of infrastructure i.e. Spatial Data Infrastructure (NSDI). This is one of the reasons that many countries are developing National Spatial Data Infrastructure (NSDI). But the challenge of developing a successful NSDI depends largely on its implementation which is so significant that none of the two key stakeholder groups i.e. public or private sectors can address it at their own. Therefore, if efforts are made to implement such initiatives by only one of the key stakeholder groups then the result may be partially if not totally failure to get the tangible benefits truly intended from such initiatives. As an example, Indian NSDI is explored in this context.
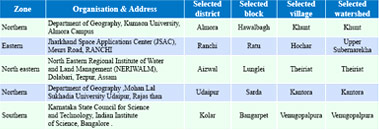
Nehru Yuva Kendra Sangathan (NYKS) , an autonomous agency under Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports has the bounden duty to achieve the objectives laid down in the National Youth Policy. The advancement in the field of Science and Technology should be made available to the youth and to the community. As the adaptation of scientific and technological principles and developments, to maximize the use of local resources, are central to empowerment in the quality of life, the Policy recognizes the importance of emerging, modern technologies, particularly in the field of information technology and electronic media, in enabling the youth to perform and achieve in all sectors of their interest.

GPs is running since more than a decade. There are user groups in all domains relying on the provided information. GPS is even used in safety critical environment, but there have been no certification of the GPS system nor are there any plans to do so. Within aviation, GPS is assumed to fulfill requirement on reliability and availability based on observations of the past. Is the discussion in Europe about certification of the Galileo SIS (Signal in Space) just another proof for the bureaucratic overhead imposed on the Galileo project? NavCert as part of the TÜV SÜD group is focused on certification in the area of positioning and navigation.

This note is about two developments in the mapping world that should be of interest to professionals in the geospatial industry. One took place in the United States where a group of surveying professionals have asked the courts for a ruling on who may be able to tender for public contracts to draw ‘maps’. This development should raise the concern of most geospatial professionals. The second took place at the opposite end of the world in Australia where the Copyright Agency representing surveyors has sought a ruling on the ownership of intellectual property rights of surveyor’s maps. While these two cases are interesting such developments are indicative both of the maturing of the geographic information (GI) profession and the willingness of professionals to assert their ‘rights’.

Opening Plenary in Allerheiligen Hofkirche
This year more nations than ever before participated in the Munich Satellite Navigation Summit 2008 which was held from February 19th to 21st in Munich, Germany. Organizer Prof. Guenter W. Hein of the Institute of Geodesy and Navigation of the University FAF Munich welcomed 400 guests from …










 (5.00 out of 5)
(5.00 out of 5)