
Intelligent map system tender by SLA
The Singapore Land Authority (SLA) has awarded the tender for the design, development and maintenance of a government-wide intelligent map system to NIIT Technologies Pvt. Ltd. The proposed solution shall be based on ESRI ArcGIS Server 9.3 and Microsoft Dot Net Technology. www.sla.gov.sg

Delhi Police to use GPS & GIS
HCL Infosystems revamped the infrastructure of Delhi Police with ICTdriven tools. The GPS-based solution will facilitate routing of emergency calls directly to PCR vehicle network operators for the scenarios that include traffic congestion, medical assistance and fire, as well as crime-in-progress situations. www.hclinfosystems.com
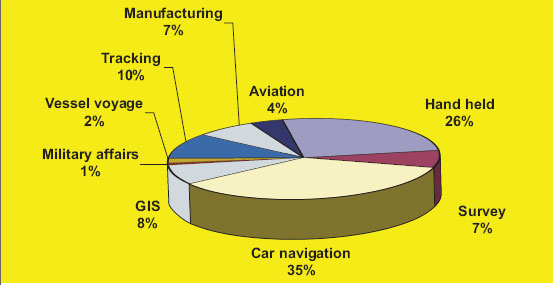
GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite Systems) is a common acronym encompassing all existing and planned satellite-based navigation systems. So far, the US-built GPS dominates the scene completely, but the Russian GLONASS is approaching around-the-clock global operational status, and other systems are being developed (the European Galileo, the Chinese Compass/Beidou and the Indian IRNSS). There are also augmentation…

IFEN to upgrade Galileo open air test bed signals
The German Aerospace Center has contracted with IFEN GmbH for the signal upgrade of the Galileo Test and Development Environment (GATE), per the latest versions of the European Space Agency’s Galileo Signal-in-Space Interface Control Document (ICD) and the GNSS Supervisory Authority Public Galileo Open Service ICD. After completion of the signal upgrade at the end of 2009, the GATE test infrastructure will be capable of transmitting the new CBOC signal structure on the Galileo E1 frequency band and a broader bandwidth of 92.07 MHz on the E5 frequency band, according to IFEN. www.ifen.com











 (5.00 out of 5)
(5.00 out of 5)