
Indian NSDI publishes Metadata Standards ver 2.0
The National Spatial Data Infrastructure (NSDI), under Department of Science & Technology of Government of India, has released Metadata Standard 2.0. It is prepared by the working group on ‘Metadata Standards’ chaired by Dr. S K Pathan, from Space Applications Centre (SAC), ISRO, Ahmadabad. The National Natural Resources Management System (NNRMS) Metadata Standards defines the schema and design for the NSDI Metadata. It also contains a set of relational tables that standardise the layer metadata, the geographic search metadata, the access metadata etc.
Metadata is the first element of the NSDI, which enables a user to find spatial data that is available in different NSDI Agency servers. It serves two major purposes – both for the spatial data generator and for the spatial data user. For the generator, it provides a framework to document the spatial data and declare its content for users. For the user, it serves many important purposes, including finding the spatial data as per need; browsing spatial data; deciding on whether the spatial data will meet the application need and finding how the spatial data can be accessed.
ISRO, with the involvement of Survey of India, National Informatics Centre, Geological Survey of India, Forest Survey of India, National Bureau of Soil Survey and Land Use Planning, National Atlas and Thematic Mapping Organisation, Central Ground Water Board, Central Water Commission and the private sector, has led the effort of defining a ‘National Metadata Standards’. http://www.nsdiindia.gov.in

Obama proposes terminating system that backs up GPS
In his fiscal 2010 budget, President Obama killed funding for a system that would back up the much relied on GPS if it failed, despite calls from the telecom industry and federal agencies that it is needed. The Homeland Security Department (DHS) endorsed Loran-C a year ago as a backup for the satellite-based GPS, but in its fiscal 2010 budget, the department zeroed out funding for the system. www.nextgov.com

Iwave launches SiRF III based GPS module in India
Iwave Systems Technologies Private Ltd has unveiled iw-GPS receiver module based on SiRF III, a low power, miniature module for Personal Navigation, fleet management, asset tracking, personal tracking, surveying, security and other navigation devices. www.iwavesystems.com
The effort for realizing fully autonomous and operative Unmanned Aerial Systems (UAS) induced the need of developing innovative techniques for integrating measurements derived from different aircraft navigation systems. Since no human aid is available onboard UAVs, navigation hardware must attain larger capabilities than the ones of manned platforms. In particular, the most important features that shall be considered are autonomy, safety,…
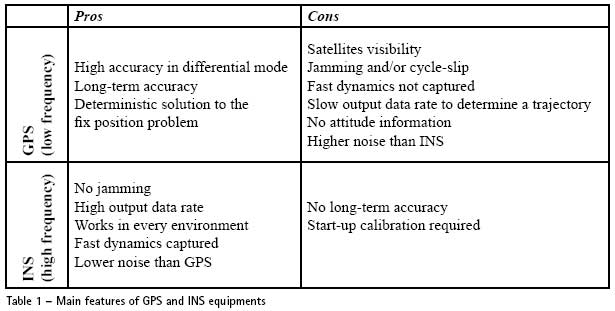
here has been a renewed interest in exploration of the moon and in the past four decades the exploration of moon has become a reality [1]. A number of missions have been flown to the moon by many countries. Many of these missions have carried imaging systems that, collectively, have returned an incredible wealth of information on the shape and surface characteristics of the moon. Mapping of moon began in the seventeenth Century by Galileo…

Oil was first commercially exploited in the North Sea in the 1960’s. Production is underpinned by regular and reliable helicopter operations enabling the movement of staff and equipment to and from the shore. However, the North Sea environment is challenging for rotorcraft operations from many perspectives, not least its remoteness from the shore, the exacting weather conditions and the changeable nature of rigs…
Contrary to the gloomy economic picture painted by the financial pundits at the end of 2008, the reactions to the global economic slowdown are mixed in the survey equipment industry in India. The growth in the survey industry has been fuelled by the spate of infrastructure projects in the country and may well ride out the economic slowdown wave without feeling the pinch much feel the players in the industry…












 (5.00 out of 5)
(5.00 out of 5)