Articles in the Articles Category

Beneath our feet in the UK lies a vast labyrinth of millions of kilometres of buried pipes and cables, delivering key products and services essential to our social and economic well-being. These networks of buried assets need repair and maintenance, and the growing demands of the UK economy mean that in years to come the networks will continue to grow significantly, as will the amount of traffic on the streets under which many of these assets lie.
There are now more companies involved in digging holes across the UK than ever before. Latest estimates put this figure at around 4 million holes dug by utility companies annually, and this excludes any excavations made as part of construction projects and works away from the street. Every time a hole is dug it impacts on traffic and the local environment. Often, holes turn out to be ‘dry’ – inaccurate information means that assets thought to be there cannot be found.

Very Long Baseline Interferometry (VLBI) is the unique space
geodetic technique which can provide the Celestial Reference Frame (CRF), the Terrestrial Reference Frame (TRF) and the relationship between the two frames — Earth Orientation Parameters (EOP) at the same time. VLBI has a widely usage in space geodetic, ground
geodetic, geophysical fields and so on. Presently, it can determine the position of the radio source outside the galaxy with 1mas precision, and determine several kilometers length of baseline on the earth’s surface with 1cm precision. Due to its high stability and high precision character, the Celestial Reference Frame outside the galaxy based on VLBI has been the best realization of the quasi-inertial referenceframe since 1980s. VLBI stations are the most important benchmarks in the International Terrestrial Reference Frame (ITRF), and VLBI is one main supporting technique which determines EOP. Till now, space and ground VLBI have accumulated more than 20 years’ data. They provide continuous and long-term data guarantee for space geodetic, ground
geodetic and geographical research.
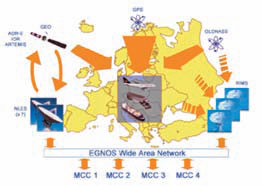
The current GPS civil service provides suitable performance only in situations of good electromagnetic visibility; the positioning becomes difficult in severely signal degraded environments, e.g. mountainous or urban areas, where a lot of GPS signals are blocked by buildings or
natural obstacles. The GPS gaps can be partially solved employing spacebased augmentations systems; in this paper we consider geostationary and geosynchronous constellations. A simulation software has been developed in MATLAB® environment in order to study the integration of existent and feasible constellations.
July 2008
International Summer Schoool on GNS
21 – 31 July
Berchtesgaden, Bavaria, Germany
http://www.munich-satellite-navigationsummerschool.
August 2008
ESRI’s 28th annual International User Conference
August 4-8, 2008 in San Diego, California
http://www.esri.com
3rd Indonesian Geo-Information …
It is a demonstration once again.
Rather, an assertion of capabilities and underlying pride.
ISRO’s Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle,
PSLV-C9, successfully launched ten satellites
together, perhaps the highest payload ever.
…

What is the Future Cities India 2020 program?
Future Cities India 2020 was inspired by the U.S.-based National Engineers Week Future City Competition. That program, which is in its 16th year, reaches more than 30,000 students annually. Bentley sponsors the Future City Competition National Finals and also chairs its …














 (5.00 out of 5)
(5.00 out of 5)