
Earth Commission: A new initiative in India
The Earth Commission — the first of its kind in any country, will pursue an integrated approach of research to tweak meteorological data for accuracy and reliability. Meteorologists, geo-physicists, oceanographers, atmospheric scientists and space scientists will pool their expertise.
CNR Rao, Chairman of the Prime Minister’s Science Advisory Council, told HT, “We have taken a holistic view of earth science. Kapil Sibal (Science and Technology Minister) has endorsed our opinion. The Prime Minister has received our report. It (the new commission) will be placed before the cabinet for approval.” The Earth Commission will be structured along the lines of the space set-up, with three rungs, namely, the Earth Commission, the Department of Earth System Science (DESS) and the Earth System Science Organisation (ESSO). The commission, its department and research organisation will have a single head, just as with the space agency.

Korea to establish satellite data center
Korea will establish a global navigational data center. The center will be linked to a global system of satellite tracking stations called IGS. The Korea Astronomy and Space Science Institute has said it has won a bid to establish the data center in Daejeon, southwest of Seoul. The center will collect data from more than 350 navigational satellite observatories worldwide and relay it to users. Korea hopes the new center will become a satellite navigation hub for Asia.
http://english.chosun.com

Spectra Precision Laser grade control systems
Trimble has introduced a portfolio of laser-based machine display and control systems for grading and excavating applications. The new Spectra Precision Laser machine systems is said to be highly fl exible, extremely rugged and can be used on a wide range of machines, including dozers, backhoes, scrapers, skid steers and excavators. On a dozer, the system can be upgraded for automatic blade control providing even greater productivity gains. The Spectra Precision Laser grade control systems give the operator visual guidance for the cutting edge of the blade or bucket.
www.trimble.com

The Great Trigonometrical Survey of India was completed in 19th century under leadership of the great surveyors- Lambton and Sir George Everest. It is inconsistent and inadequate. Accuracy of the network is only of the 1st order or less. First order was defined as better than only 1 in 50,000 only. Reference surface and Datum- The Everest Spheroid was given by Sir George Everest in 1830. Center of Everest Spheroid is about a km away from the center of gravity of the Earth; hence it is non-geocentric. Thus it is inaccurate and unsuitable under present circumstances. Leveling network of India has inconsistencies. Gravity observations were not carried out and not taken in to consideration. It was not appropriately adjusted. Indian Absolute Gravity Datum does not exist. Absolute gravimeters have not yet been used to define Gravity Datum in India. Topographical maps are on Polyconic projection. Assumptions and approximations accepted make it a non-projection. The earth is assumed to be fiat and there are no distortions of any kind. The projection has created problems in digitization, compilation and integration of maps. Design of the Grid adopted in India is not satisfactory. Distortion at central parallel is 1 in 824, which is quite high. There is archaic Restriction policy, which is not transparent and hinders research and development India has to make a choice between chaos and development. These problems have been discussed in detail in this paper. How India should go about to establish new geodetic infrastructure for systematic development and research, has been described in this paper.
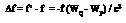
Conventionally, the potential difference between two points P and Q located on the Earth’s surface are determined by gravimetry and levelling (Heiskanen and Moritz 1967), the drawback of which is that it is almost impossible to connect these two points in the case that they are located on two continents, because it is well known that the potential surface of the mean sea level (MSL) is not an equipotential surface. In another aspect, if given the gravity data on the Earth’s surface, one might determine the potential difference between two points by using the Stokes method or Molodensky method (ibid). In this case the potential field is determined and consequently the potential difference between two arbitrary points could be determined.
26th ACRS 2005, 7-11, November, 2005 Hanoi, Vietnam
The 26th Asian Conference on Remote Sensing (ACRS) and 2nd …











 (5.00 out of 5)
(5.00 out of 5)