December 2008
GEOExpo 2008 China
2 – 4 December 2008,
Shanghai, China
sales@chinageo-expo.com
http://www.ChinaGeo-Expo.com
January 2009
ESRI Asia Pacific User Conference
20-21 January 2009
Singapore city,Singapore
http://www.esri.com/events/apuc/index.html
Intergeo East
27-29 January 2009
Istanbul,Turkey
http://www.intergeo-east.com
February 2009
Trimble Dimension 2009
123-25, February 2009
The Mirage, Las Vegas, USA
http://www.trimbleevents.com/dimensions09
March 2009
Munich Satellite Navigation Summit Conference
March 3-5,2009
Munich, Germany
http://www.munich-satellite-navigation-summit.org
April 2009
GEO Siberia 2009
21-23 April
Novosibirsk, Russian
nenash@sibfair.ru
http://www.geosiberia.sibfair.ru
May 2009
International Conference on …

The future of the surveying profession is an issue that has been lingering for many years. Recently, the concern has been growing wider and louder among surveyors. Some surveyors contend that the surveying profession, in its current form, is heading towards extinction. Their reasons include a gradual decline in the number of qualified and licensed professionals, impact of emerging technologies, sophisticated and more capable equipment…
The Terrain Mapping camera (TMC) on board Chandrayaan-1 spacecraft was successfully operated on October 29, 2008 through a series of commands issued from the Spacecraft Control Centre of ISRO Telemetry, Tracking and Command Network (ISTRAC) at Bangalore. Analysis of the first imagery received by the Indian Deep Space Network (IDSN) at Byalalu and later processed…

At SatNav, we have had the privilege of seeing the Indian GPS Navigation Industry from the year 2002, the time we launched our first voice based system, when comments like ‘who needs it?’, ‘my driver knows all the places’, ‘I prefer asking a panwallah to such devices’were the norm. Today the world has changed where the comments are, ‘why doesn’t it tell me the right way to my home?’ and ‘it’s a useful product’, ‘we appreciate…
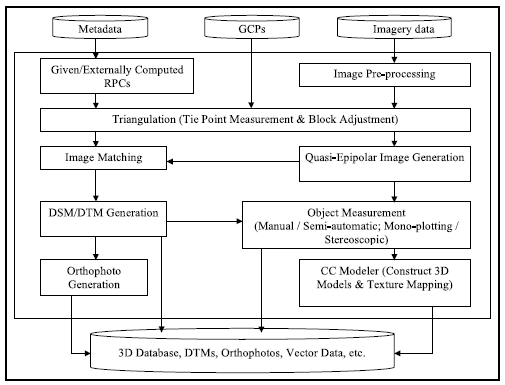
Earth-observation techniques attract currently a substantial amount of interest and open fresh research and business opportunities for the geospatial community. They offer nowadays a broad spectrum of diverse platforms, sensors and products. UAV systems are paving their way into novel applications. The development of large format digital aerial camera systems has triggered a renewed interest in aerial photogrammetry…
The moon mission of India.
A display of technological prowess.
And willingness.
On November 4, Chandrayaan-1 …
The issue of FDI in GPS systems came up recently in a series of meetings held by the foreign investment promotion board (FIPB). Of late, many Indian companies have evinced interest to manufacture GPS devices in joint venture with foreign counterparts. http://economictimes.indiatimes.com












 (5.00 out of 5)
(5.00 out of 5)