| GIS | |
Using geomatics to fight the pandemic in Italy: A case study
Integration of GNSS with modern GIS tools for the governance of the vaccination infrastructure in Italy |
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
On December 2020, the Italian Public Administration requested the governance of a project aiming in the creation of the digital infrastructure needed to support the anti-Covid-19 vaccination. Among the most important objectives of the project was the real time, multistakeholder accountability, with both push and pull information, about the state of installation and operativity of all the mobile digital assets involved 5 Italian Regions. To guarantee these objectives, having to deal with a project of a national extension, members of the team designed and proposed a multi-disciplinary solution, integrating positioning data and GIS features under the recently released reporting platform, Microsoft Power BI. The specific technical aim has been to provide an interactive reporting dashboard, with multi-level accountability and controlled accessibility, that features real-time updating on the operativity of all assets in the network, their positioning and states, calculated from A-GNSS observations and Gyro-INS data that are managed in a mobile android APP environment. The designed architecture is fast to develop, highly versatile and customizable. For this reason, mostly plug-and-play, both hardware and software components have been chosen and used to provide accurate, real-time, and effective reporting on the global advancement and operativity of the project according to the specific needs of each stakeholder group. The case study evidenced the powerful opportunities offered today by commercial tools that convey geomatic principles and techniques into more versatile, integrable and contextless applications. In addition, the paper tried to evidence that, even if the applicability of these tools is immediate, there is still need to cultivate a certain knowledge of the traditional principles of geomatics, that when used accordingly, can provide very interesting and valuable solutions.
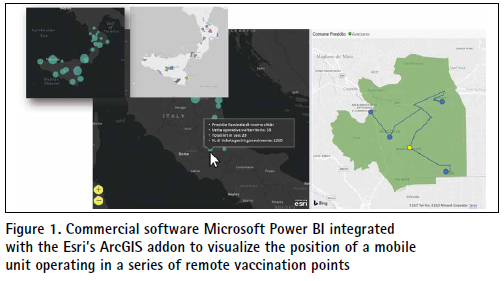
Geomatics means… integration
Digital transformation, since a couple of decades, has been revolutionizing most areas of human lives making available, applications that some years before were considered expensive, complex in their use and difficult to integrate. Advances in information and Communication technologies (ICT), were able not only to absorb these recent inventions, like sensors and algorithms, but also to focus in their integrability and usesimplification, releasing them in many cases as plug & play components with user-friendly interphases and compatibility with commercial software. In geosciences though, the need to guarantee interdisciplinarity, had been widely observed from researchers even earlier in many practical applications (Elaiopoulos et. al., 2012). For instance, someone could think of the GNSS positioning to geo-reference space-born earth observations (Dominici et. al., 2013), the classic fusion of Synthetic Aperture Radar data (SAR) with Optical Sensors to bypass cloudy targets or to deal with observations at night (Stroppiana et al., 2015), the statistical compensation of ground-based surveys along with static positioning to improve the grade of hyperdetermination in ground deformation monitoring campaigns (Dominici et. al., 2011), or even the present case, technically consisting in the use of commercial GIS solutions with Assisted-GPS data and Giro-INS observations from sensors installed in mobile devices (tablets and netbooks), to improve reporting and thus, the overall governance of the vaccination infrastructure in Italy.
Designing the governance to convey Geomatics
Reporting activities in governance projects featuring activities with geographic extensions is a complex and important issue for most stakeholders. Especially when advisory & consulting enterprises are in charge of the coordination, real time data processing and reporting, all of the used and provided information must be guaranteed for their precision, accuracy, and level of detail, according to the involved stakeholders’ needs. At the same time, quality and validation standards of all transmitted information have to be met and not much time for manual operations is usually available. An even more complex scenario is the one concerning public administrations, like ministries, the national healthcare system and an extended network of public entities cooperating in the whole territory. The present case-study had all the aforementioned characteristics as entities would belong to at least four different ministries to be accounted for different aspects of the project’s governance and advancements. To enable in this scope the value and benefits available in the geosciences, the whole governance process of this project could be structured using a 3-phase, state modelled approach, according to which, each step, is represented by one specific milestone that could be met with a specific set of conditions:
(a) requirements elicitation to be gathered from the last mile of the sanitary structures (number of vaccination units, morphological information and dimensions of the covered area, mobile units’ needs regarding power supply and Wi-Fi coverage, administrative accountability etc.),
(b) predisposition, logistics and handling of the digital assets to guarantee the vaccination mobile unit’s needs (mobile thermal printers, wireless barcode readers, tablets, netbooks, Wi-Fi mobile routers, etc.),
(c) the governance of the installation, issues management, integration and startup of all devices in the interested territories both in hospitals and in remote units.
In some parts of the process, the set of conditions to be met is provided by the onboard sensors of the device (Gyro/ Ins/GNSS). The processing of all data was designed to be done into an android mobile APP environment enabling their parametrization as an input spreadsheet to be read by the power BI tool. The last one should be interrogated periodically by various dashboards, adequately precustomized according to the needs of each stakeholder. The dashboards would be finally shared directly as Microsoft Teams Tabs with respect and limitations to the accountability level of each stakeholder group, his or her institution and role in the project. Thus, from and architectonical point of view, the solution has been designed to guarantee a constant flow of information directly to the Microsoft Teams application of each stakeholder.
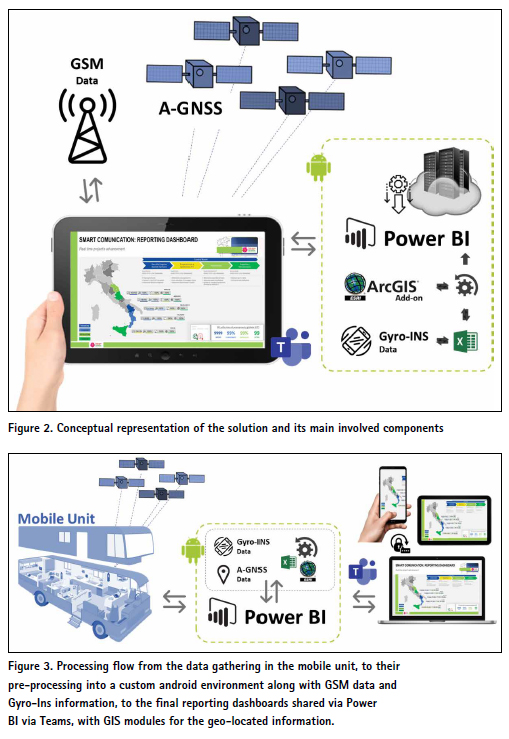
Deliverables and discussion
The key feature of the deliverable was designed to be its ability to handle the complexity of many institutions involved with the supply, distribution, installation, management and use of mobile assets constantly operating around the country. in particular, the fact that assets may be used, owned, and managed by different entities, emerge the need to design a central governance that accounts separately each involved entity, with specific reports including actual position, state and operativity of all units.
Thanks to the navigable information in GIS environment, stakeholders have the freedom to interrogate the system for specific information, without the risk to enter in conflict with other divisions thanks to the various layers and the access levels pre-designed for all stakeholders’ groups. Responsibility issues are also seem to be quite manageable with the proposed solution as administrative owners of the assets are able to observe in real time where the assets of their responsibility are located, their state of operation, the operators that accompany the assets and the future locations that are released by the planning department.
Among the benefits of the project’s government is the fact that the solution features some planning abilities consisting in pre-designed KPIs that calculate the volumes of the operativity, the future needs in terms of consumables and supplies, as well as, the grade of advancement of all operation at present and in future instances. Another quite promising aspect has been the choice to design most components (except from the android supporting APP) using commercial tool mostly developed by major software providers as Microsoft. Under critical situations like the one of a pandemic strike, this choice speeded up the whole project both because of the existing and easily accessible knowledge and with for their fast integration, especially with respect to custom solutions that need development from scratch. Regarding the final result, a certain number of constrains with respect to the customizability to the various needs was considered even if during the first weeks of application test it has not yet appeared.
References
Elaiopoulos, M., Dominici, D., Rosciano E., Alicandro M., 2012. Versatile and Interactive Surveying Methodologies to Provide Specific Topographic Solutions. Case of Study: Evaluating A Radio Antenna’s Prototype. International Federation of Surveyors. FIG Working Week – Rome, Italy, 4-5 May 2012
Abdalla, R., 2018. Urbanization and Crisis Management Using Geomatics Technologies. Crisis Management – Theory and Practice. DOI: 10.5772/intechopen.76415.
Franch-Pardo, I., Napoletano, B., Rosete-Verges, F. and Billa, L., 2020. Spatial analysis and GIS in the study of COVID-19. A review. Science of The Total Environment, 739, p.140033.
D. Dominici, E. Rosciano, M. Alicandro, M. Elaiopoulos, S. Trigliozzi and V. Massimi, “Cultural heritage documentation using geomatic techniques: Case study: San Basilio’s monastery, L’Aquila,” 2013 Digital Heritage International Congress Marseille, France, 2013, pp. 211-214, doi: 10.1109/DigitalHeritage.2013.6743735.
Stroppiana, D., Azar, R., Calò, F., Pepe, A., Imperatore, P., Boschetti, M., Silva, J., Brivio, P. and Lanari, R., 2015. Integration of Optical and SAR Data for Burned Area Mapping in Mediterranean Regions. Remote Sensing, 7(2), pp.1320-1345.
Dominici, D., Galeota, D., Gregori, A., Rosciano, E., Alicandro, M. and, Elaiopoulos, M. Using new techniques of geomatic and structural control in the old city center of L’Aquila after the April 6, 2009 earthquake. Joint International Symposium on Deformation Monitoring, Hong Kong, Nov. 2011











 (No Ratings Yet)
(No Ratings Yet)






Leave your response!