
$2.4 million for satellite imaging
Mr. Gary Lunn, Minister of Natural Resources, announced a five-year, $2.4-million project to provide access to new, high-quality satellite images of Canada and also the improved and standardized satellite images will be available to all Canadians for free over the Internet.
The newer and higher-quality images will be used for mapping, monitoring Canadian wetland areas and managing natural resources, and will support government decision and policy makers in the fields of public safety, health and the environment, as well as our northern and Aboriginal communities. Natural Resources Canada will coordinate and manage the project, ensure the quality of the data and liaise with the contractors, TELUS Corporation and Iunctus Geomatics Corp., who are supplying the satellite images.
www.NRCan.gc.ca

Geospatial industry poised for growth
Information systems alone, based on maps and satellite imagery is set to touch Rs 576 crore by 2010. At present, the market estimates for these services are Rs 12 crore. The optimism is based on the current growth rates of around 200 per cent and the huge potential. Geospatial Today and Spatial India, geospatial publications in association with Antrix Corporation and Survey of India, have brought out the report. According to the highlights of the report, the domestic market estimates for these geospatial services amounted to about Rs 562 crore in the financial year 2005. The market for these services is expected to grow at a CAGR of 17.57 per cent per annum and reach Rs 1,824.98 crore by year 2010. The key driver for this increased growth is the expected investments in land information systems (ILIS) in several states of the country. It also provides an optimistic overview in as much as the total market in our country (domestic and exports markets) is expected to record a potential growth from Rs 962 crore in the year 2005 to Rs 2,820.30 crore at a CAGR of 14.5 per cent. India has emerged as a major data conversion centre for geospatial services. In FY 2005, this sector marked Rs 720 crore with an expected growth rate of 20 per cent.
www.blonnet.com
july 2006
GeoWeb 2006
24 – 28 July, Vancouver, BC, Canada
khenton@gita.org
2006 IEEE International Geoscience …
David Sharp was left to die.
Many saw him.
They didn’t do anything.
Perhaps they could not.
Perhaps it was ‘impossible’ to do …

Indonesian military plane to map quake-hit areas
The Indonesian Defence Forces (TNI) have assigned a CN-235 airplane to carry out aerial photography on areas in the Yogyakarta region affected by 27 May 5.9-magnitude earthquake. The activity is aimed at making a detailed map of areas devastated by the quake.
TNI had also sent a Hercules C-130 plane carrying a TNI field medical team and three helicopters to evacuate victims.http://news.xinhuanet.com

MyRTKnet: Get set and go! DATO’ HAMID ALI, AHMAD FAUZI NORDIN, DR SAMAD HJ ABU, CHANG LENG HUA
A new move(ment) JG KRISHNAYYA AND GEORGE CHO
Space-based positioning system with no on-board atomic clocks FABRIZIO TAPPERO, ANDREW DEMPSTER, TOSHIAKI IWATA
Going hand in hand MADHAV N KULKARNI AND DM SATALE
India’s phone coordinates MUNEENDRA KUMAR

Galileo – the European Programme for Global Navigation Services for civil purposes is an initiative led by European Union. We provide regular updates to our readers on the Galileo programme.
Galileo OS SIS ICD now available on-line The information contained in the Galileo Open Service Signal In Space Interface Control Document (SIS ICD) is made available to the public by the Galileo Joint Undertaking (GJU), an undertaking jointly created by the European Commission and the European Space Agency. www.galileoju.com
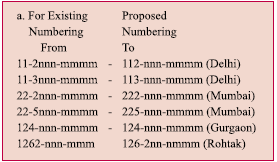
In India, the “extra” digits in telephone numbers have been added a number of times e.g., the digits for Delhi have changed from 5 to 8 in the past five decades. However, with the addition of extra digit of “2” (or “3” or “5”) in the phone numbers of the cities around the countries in December 2002, the total number has reached to “10”, i.e., “2, 3, or 4” digits of city codes plus “8, 7, or 6” digits of phone numbers. In one colony of Delhi, since…











 (5.00 out of 5)
(5.00 out of 5)