
GPS has demonstrated a stellar performance ever since its inception. In fact the satellites typically operate beyond their expected lifetime which potentially creates obstacles to the timely modernization of the system. GPSGAP (GPS, Geodesy and Application Program) is an online educational initiative by the University of Maine that offers in-depth knowledge about this fantastic system and its uses.
My enthusiasm for GPS began when testing the experimental Macrometer receiver during the summer of 1982 at M.I.T. over a 30 km baseline from Woburn, MA, to Mount Watchusett. The satellite visibility ranged from about 6 p.m. to midnight in New England. Many of the sunset watchers at the summit were puzzled by my activities and impressed by the huge piece of equipment in the back of my station wagon, the abundance of cables, and the strange looking antenna (so they thought). Their puzzlement about what I was up to was refl ected in some of their comments, such as“Is this thing taking off?”, or “Are you on our side?” Of course, there was plenty of time until midnight to be entertained by Fourier transforms and such on the computer screen, and to ponder the unlimited potential of GPS. Whatever has evolved since those days in terms of civil uses of GPS needs no further explanation.
In India, for topographical mapping, we are using an old Geodetic Datum (reference ellipsoid on which the coordinates: Latitude and Longitude are projected, and mapping is carried out), called Everest 1880, defined by the work of Col. George Everest (one of the greatest Geodesists, for whom the highest peak in the world is named). It is a local datum, best-fi tting for India (as in 1880), but not fi tting the Earth as a whole in the best possible manner.
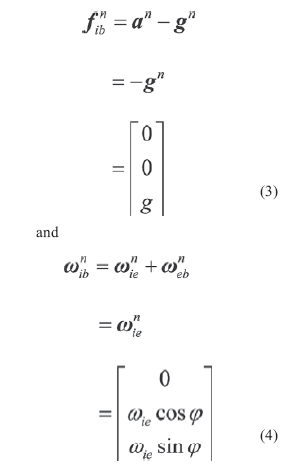
The object of the SINS selfalignment is to determine the direction cosine of the transformation from the body frame to the navigation frame, namely, the elements of initial attitude matrix, using the accelerometer and gyro outputs. As the alignment accuracy affects the accuracy of the navigation system directly, one of the most important requirements of SINS alignment is high alignment accuracy. In many practical applications, SINS alignment also requires high alignment speed and the capability of self-determination, especially for military applications.
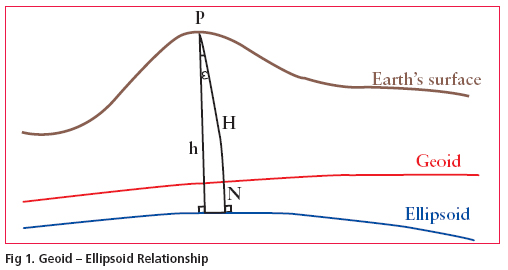
The demand for a high resolution geoid model has grown substantially during the last few decades especially after inception of Global Positioning System (GPS). Many countries across the world have already developed their own geoidal model which serve as the means of deriving orthometric heights from GPS observations. The impact of GPS on surveying application is undeniable. More so, this revolution has not been confi ned to the surveying community, but has extended into mapping, navigation and Geographic information system (GIS) areas. During the last few years, we have been witnessing the wide spread adoption of GPS with an equivalently
vibrant range of accuracy requirement. Many of these applications require accurate vertical positions.
The task of transforming the ellipsoidal height obtained from GPS technique to the orthometric height has prompted geodesists around the world to determine the high precision geoid undulations, for their region of interest. In India the present day nation wide geoid was computed a long time back and based on astro geodetic observations with respect to Everest spheroid. It has various limitations and does not have any signifi cance as far as GPS solutions for orthometric height is concerned.

Today’s professional navigators may well be the last. As recently as a generation ago, navigation was almost solely the specialised art of a small number of highly-skilled people. They wore uniforms with emblems on their shoulders. They had years of training.They used complex, expensive, equipment. They bestrode the bridges of ships and the fl ight decks of the large commercial aircraft and took star shots.

Sales contract from Cessna Aircraft Company to Leica
The Metrology Division of Leica Geosystems, Switzerland announced USA based Cessna Aircraft Company, a Textron company, has signed a sales contract for eight portable Leica Geosystems CMM systems used for industrial measurement and inspection. The acquisition consists of four Leica LTD840 Laser Trackers, and four Leica LTD640 Laser Trackers. Cessna is a manufacturer of general aviation airplanes. Leica Geosystems’ 3D coordinate measurement systems are used by manufacturers worldwide in the aerospace, automotive and shipbuilding industries. www.leica-geosystems.com
On Jan 10, India leaped high in space with the successful launch of its tenth Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV-C7) that put …
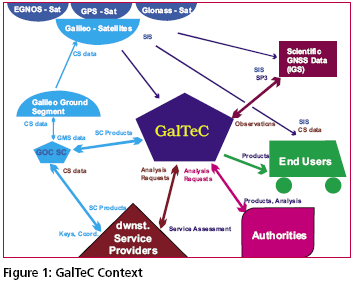
Today Satellite Based Navigation Services play an increasingly important role in modern society. The provision of the navigation, positioning and timing service provided by GPS is widely used. However, the system is under military control, and consequently legal guarantees of operation required by modern business cannot be given. On the other hand the market for GNSS related products is recognised as an important economic factor and service guarantees and liabilities will be needed.
I am an avid outdoor enthusiast and as such got a very simple GPS handset as a gift from a friend visiting me from abroad. This GPS can simply tell me my location in terms of latitude and longitude anywhere on earth. It can also help me trace back my route if I am lost in say a jungle or desert etc. The device is intended for use outdoors just for fun.
A few friends told me that apparently I need a license to use this device in India. I did some internet based research to find out the truth behind the matter and came across your magazine where you had printed an interview of Mr P K Garg, Wireless Adviser to Government of India, Wireless Planning and Coordination (WPC) Wing, Ministry of Communications and IT, Government of India. Although I was surprised to read that yes indeed I needed a license to operate the device in India, as confirmed by Mr Garg, being a law abiding citizen I decided I must acquire the license before operating it or at least apply for it. This started off a very frustrating process for me of trying to crack the bureaucracy which I am relating below in the hope that it will be read by someone who is authoritative enough to help me out.

The U.S. National Space Policy (NSP) was authorised by President Bush on August 31, 2006. This NSP establishes an overarching national policy that governs the conduct of U.S. space activities and supersedes the 1996 NSP.
The unclassified ten-page summary of the NSP consists of 13 self-contained sections including the principles, goals, guidelines (both general and specific to national security space, civil space and commercial space), international space cooperation, space nuclear power, radio frequency spectrum, orbital debris, effective export policies and space-related security classification.







 (5.00 out of 5)
(5.00 out of 5)