| Surveying | |
MyRTKnet: Get set and go!
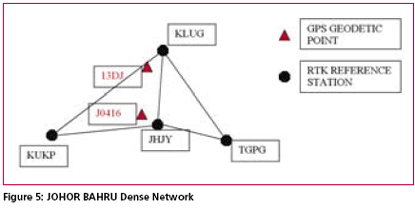
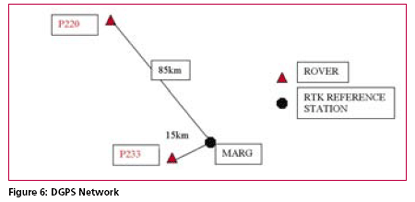
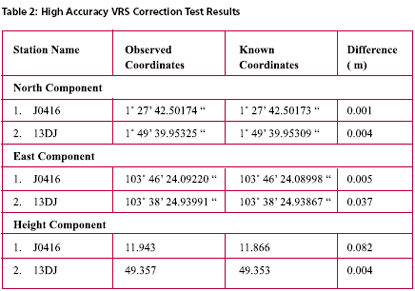
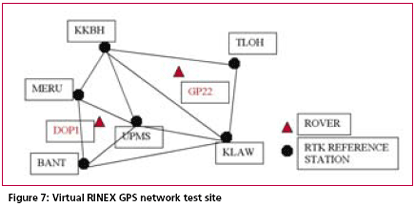
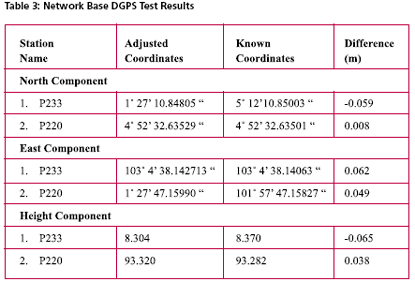
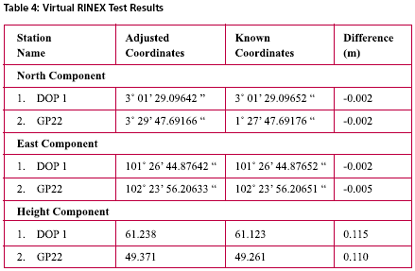
Possible Field ApplicationsMyRTKnet services can be used for various surveying applications ranging from setting up of control to the detailing of project sites; its usage will benefit surveyors and many other GPS users who rely on these utilities to locate their positions. The following are some of the possible field applications of MyRTKnet services: MyRTKnet testingCase study for high accuracy VRS correction testa. The objective of the High Accuracy VRS Correction Test is to compare GPS observed coordinates with their corresponding published GPS geodetic values. The test was carried out at the existing GPS geodetic network in the Dense Network. An example of the layout of the network test site is shown in Figure 5. b. The Dense Network consists of 3 sites located at Klang Valley, Penang and Johor Bahru. For this case study, Johor Bahru Dense Network was selected .This site comprises of four (4) GPS reference stations (known stations) namely KUKP, JHJY, TGPG and KLUG. The test was carried out using VRS technique with 5 sessions of observation (consisting of 10 measurements in each session) on 2 GPS receivers. c. Dual frequency GPS receivers were used in the test with the observation d. The final observed coordinates values as mentioned in table 2 were the results of the average of the whole set of observations. e. The results show that the accuracies in the horizontal and height component were less than 1 cm and 9 cm respectively. It also shows that for areas within 30 km from the network, the accuracies obtained were within the said levels. tableCase study for Network base DGPS correction test a. The objective of the Network Base DGPS Correction Test is to compare GPS observed coordinates with their corresponding published GPS geodetic values. The test was carried out at the existing GPS geodetic network in Peninsular Network. An example of the layout of the network test site is shown in Figure 6. b. The MARG (Marang) Reference Station in Terengganu is used for the test. The test was carried out using Network Base Differential GPS (DGPS) technique with 5 sessions of observation (consisting of 10 measurements in each session) on 2 GPS receivers. c. Two dual frequency GPS receivers were used in the test. The observation criteria applied was similar to the test (case study for high accuracy VRS correction test). d. The final observed coordinates values as mentioned in table 3 were the results of the average of the whole set of observations. e. The results show that the accuracies in the horizontal and height component were between 1 to 6 cm and 3 to 6 cm respectively. It also shows that for areas within 30 km from the network, the accuracies obtained were within the said levels. Case study for Virtual RINEX testa. The objective of the Virtual RINEX Data Test is to compare the GPS coordinates obtained from the processing of the Virtual RINEX data with their corresponding published GPS geodetic values. The test was carried out at the existing GPS geodetic network in Peninsular Network. An example of the layout of the network test site is shown in Figure 7. b. The Network site comprises of six (6) GPS reference stations (known stations) namely KKBH, MERU, UPMS, BANT, KLAW and TLOH. The test was carried out using GPS Static technique with 2 sessions of 10 minutes on 2 GPS receivers. c. Two dual frequency GPS receivers were used in the test. The observation criteria applied was similar to the test (case study for high accuracy VRS correction test). d. The comparison of the final adjusted coordinates and the published coordinates are as follows as mentioned in table 4. e. Results show that the accuracies in the horizontal and height component were between 1 to 2 cm and 10 cm respectively, and that for areas within 30 km from the network, the accuracies obtained were within the said levels. ConclusionThis paper introduces a new GPS positioning by way of RTK-GPS (VRS) using MyRTKnet services provided by DSMM. MyRTKnet has been successfully implemented with the establishment of a Network of Reference Stations equipped with GPS receiver, antenna, communication server/router, software, power supply, UPS, lightning arrestor and other accessories and equipments necessary for the full working of the station. A Control Centre has also been established equipped with computation server, software, power supply, UPS, communication router/server, Web server and other accessories and equipment necessary for the operations of the facility. The precision estimation of positioning results surveyed by VRS has also been verified. Outcome of field experiments shows that standard deviations of 3- components of real-time positioning by VRS are about ±2 cm in horizontal and less than ±4 cm in vertical and this meets the demand for survey precision of local control point. Network DGPS solutions have also been tested with results showing that sub-meter applications were possible in areas where VRS correction are not available. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
















 (No Ratings Yet)
(No Ratings Yet)



