World Hydrographic Day is being celebrated on the 21st June every year to commemorate the establishment of the International Hydrographic Bureau by 19 member states in 1921 at the Principality of Monaco at the invitation of HSH Prince Albert I, a noted marine scientist and oceanographer, who had graciously offered the requisite space and facilities free of cost. In 1970, it was renamed as the International Hydrographic Organisation (IHO) and has presently 80 Member States, covering the vast majority of Ocean States. IHO plays a very useful role in Standardisation, International Charts, Capacity Building and Technical Cooperation, Education and Training, Hydrographic Surveying, Charts (paper and digital), Regional Hydrographic Commissions, Cooperation with other International Organisations, Tsunami Information, and nautical Publications.
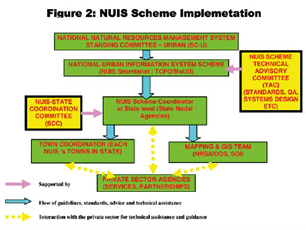
State of the art global communication technologies and thriving economy is facilitating Indian cities to compete in the global environment. The constant transformation of urban areas into complex entities has brought forth new challenges and opportunities for Planners to design and implement a variety of activities in spatial terms. There is need to tread common ground so as to address problems and issues in the right perspective to assist cities in coping with economic realities and thereby produce high quality responsive environment and demonstrate successful urban solutions.
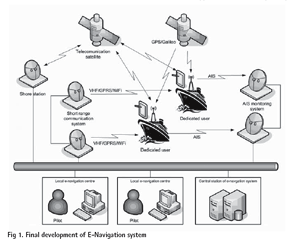
The common objective shared by all the Member States of IMO (International Maritime Organization) is a commitment to deliver safe, secure and effi cient shipping on clean oceans. The co-sponsors of this submission believe that IMO now has an opportunity to develop and map out a clear strategic vision for one common integrating and utilizing all the navigational technological tools at our disposal to secure a greater level of safety and incident prevention which will, at the same time, deliver substantial operating efficiencies with resulting commercial benefi ts, whilst also continuing to respect the freedom of navigation rights.
July 2007
Cambridge Conference 2007
15-20 July Cambridge, UK
www.ordnancesurvey.co.uk/
Asia Oceania Geosciences Society, 4th Annual Meeting
30 July – 3 August, Bangkok, Thailand
August 2007
7th International Workshop of Geographical Information System
1-3 August Beijing, China
iwgis@lreis.ac.cn
XXIII International Cartographic Conference
4-10 August, Moscow, Russia
info@icc2007.com.
GIS 14 Conference
14-15 August 2007
Vietnam
2nd Indonesian Geospatial Technology Exhibition
29 August – 1 September
Bakosurtanal; Jakarta
http://www.geospatial-exh.com/
September 2007
51st Photogrammetric Week
3-7 September
Stuttgart, Germany
martina.kroma@ifp.uni-stuttgart.de
http://www.ifp.uni-stuttgart.de/favicon.ico
INTERGEO …

NovAtel Inc launches new OEMV products
NovAtel has launched its new OEMV-1G and FlexPak(TM)-V1G products with GPS+GLONASS positioning solutions. Also, full GPS+GLONASS AdVance RTK (Real Time Kinematic) positioning capabilities are available on all existing OEMV-2 and OEMV- 3 products via its 3.2 Firmware release. www.novatel.com.
Prof Madhav N Kulakrni.
A member of Coordinates family.
We had been fortunate to have his guidance for last two years.
His sudden demise has left us in shock.
His name itself was synonym of GPS/Geodesy in India.
An irreparable loss to GPS community and science.
We share our heartfelt grief with the bereaved family and pray for strength to …
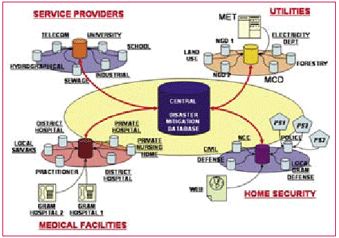
In recent past , humanity has suffered an increasing number of natural disasters affecting more than 2.5billion people, killing 478,100 and causing economic losses of about US$690bn (UNEP/ GRID-Arendal, 2005). Some of the distinctive instances are: December 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and its concomitant tsunamis, The US eastern coast and Central America, hurricanes Katrina, Rita, Mitch, Stan and Wilma in September-October 2005, Pakistani earthquake of 2005, and now the current avian influenza in Asia and Europe. Natural and manmade tragedies, such as earthquakes, foods, nuclear catastrophes, pose an ever-present challenge to emergency services. Victims and societies at large have responded differently in each case. Some were heroic, some responsible but many panicked and responded irrationally. This aggravated the already bad situation. All of them could have responded more effectively if they were better informed and aright managed.

In sudden and untimely demise of young Prof. Madhav Kulkarni, Indiahas lost the best and boldest geodesists. Proud of the glorious past, he wanted that independent SOI should achieve GREAT of its own. For his reverence to Everest, he was trying to achieve the new 21st century Indian Geodetic System as “Everest 2007”. …

Exact determination of position, at any time, from any location, secure and precise navigation, efficient route planning – in the future it will all be summed up in one word: Galileo. This new European navigation system with 30 satellites will be ready for use in the beginning of the next decade. A first test satellite has been launched into its orbit in 2005. Another one will follow by the end of this year. Galileo will make civil users of satellite navigation in Europe and all over the world independent of the American Global Positioning System (GPS). Even more, especially in connection with civilian use, Galileo will outperform GPS and thereby open the gate for new applications and markets for satellite supported navigation. Especially in the combination with navigation, mobile telecommunication and information services, there is an immense utilisation and market potential.










 (5.00 out of 5)
(5.00 out of 5)