Articles in the Applications Category

The Solutions for Open Land Administration (SOLA) Open Source Software project is a 3 year trust fund project, funded through the Government of Finland and implemented by a project team within the UN FAO.
Its aim is to make computerized cadastre and registration systems based on open source software more affordable and more sustainable in developing countries.

Disaster management is a widely discussed topic around the world and more so in recent years because of large scale disasters experienced around the globe. Most discussions appear to be siloed to a particular field of expertise although it is well recognised that a coordinated effort is required amongst

Nowadays researchers and various users are very interested in urban applications at large scale, where small UAVs are very useful. In Photogrammetry, UAVs represent a very fl exible and low-cost platform which reduces data acquisition time and provides for high resolution and high accuracy data for small area modeling…

Pilotless aerial vehicle systems (PAVs) have captured many people’s imaginations through the media as combat vehicles in various war zones around the world. These vehicles of combat have acquired the pejorative term ‘drone’ as these aircraft have ‘no intelligence’ and only respond by attacking positions identified by forward personnel on the ground…

Imagine a country without any basic administration of land – their key asset. Imagine that tenure to land and property cannot be secured, and that mortgage loans cannot be established as a basis for property improvement. Imagine that the use and development of land is not controlled through overallplanning policies and regulations.
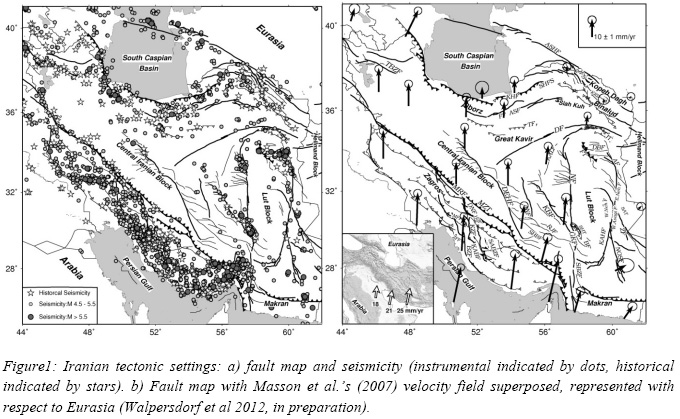
Large scale seasonal atmospheric correction will be investigated using ERA-Interim meteorological model and GPS data. A twisted plane is also fitted to remove orbital errors. To investigate the long wavelength tectonic signal due to interseismic strain accumulation, a time series analysis of the selected Images has been done on a pixel basisin order to enhance signal to noise ratio affected by remaining atmospheric signal.













 (5.00 out of 5)
(5.00 out of 5)