Articles tagged with: Akio Yasuda

A S (quasi-zenith satellite), which was anticipated to be the original Japanese positioning satellite, was launched in September, 2010. As an augmentation system of GNSS, two MTSATs had already been put into orbit and their main purpose is to broadcast the correction data for wide-area DGPS. This has actually improved the accuracy of wide area DGPS as a result of reception of the correction data from MSAS (MTSAT Satellite-based Augmentation System). The QZS also enhances the ranging function and it already has signal characteristics for the GNSS that are expected in the near future.

MSAS (MTSAT Satellite-based Augmentation System is the Japanese satellite based augmentation system which has been prepared by the Civil Aviation Bureau of Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism (MILT) and started on 27 September 2007, to serve for improving accuracy, integrity, and availability of GPS positioning on the civil aircrafts. It has two geostationary satellites, called MTSAT-1R and MTSAT-2 located at 140 and 145 degrees in the east longitude, on the orbit of 3600km above the Equator. The satellites were launched in February of 2005 and 2006 respectively, long after the launch failure on November 1999. MTSAT, which stands for Multi-functional Transport SATellite, also has a function of geostationary metrological satellite.
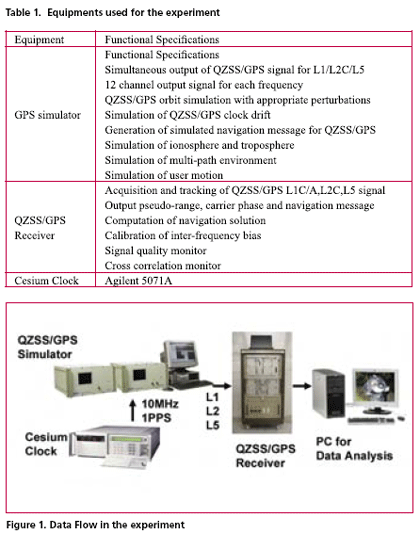
GPS modernization will expand the area of positioning service and will increase its convenience. Particularly, the third civil frequency namely L5, which will be provided by both modernized GPS and QZSS, is expected to improve the performance of precise positioning using carrier phase observation. This paper reports an experimental result regarding the convenience of additional L5 signal. Actual navigation signals generated from GPS simulator were received by triple frequency GPS receiver in the experiment. Navigation data, pseudo-range and carrier phase observation have been obtained and used for the analysis. This experiment verifies the improvement of ambiguity fixing time and multi-path mitigation using three frequency signals.










 (5.00 out of 5)
(5.00 out of 5)