| GNSS | |
Low cost optimized GNSS application
Today global navigation systems have become a part of our everyday life. It is part of many useful things and assisted people in many ways. It is part of the marine, aircraft and traffic issues – from private user up to logistic cooperation. Also it is used in agricultural companies for precise farming as well as for information systems in all kind of tasks like geology, archeology, hydrology and a lot more. In the sector of engineering, it supports and guides the construction machines. Diverse scientific experiments and duties utilize GPS as part of their time measuring systems. In the field of survey, the exploit broadness is also widely spread. MotivationThe main motivation is to provide a solution for engineering professionals but with a mass market-based Android application platform. So, combining simplicity in handling with object orientated databases – where targets can be addressed and edited. It can be used by people without special surveyor education but produces outcomes that can further be used in high end solutions. A qualified post processing is possible any time.
At the time, we combine tablet PC’s that have the application and already have an internal GPS chip (in some cases an AGPS) or for higher precision OEM GPS receiver via Bluetooth (see figure 2).
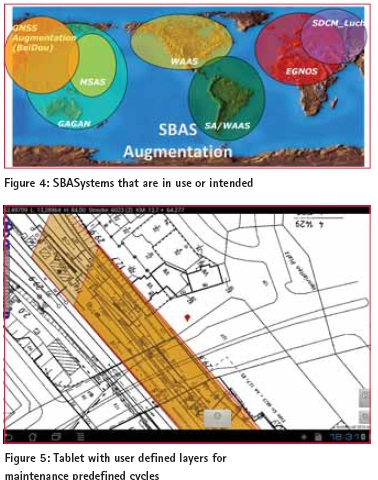
FundamentalsGNSS is the term for a global navigation satellite system that consists of several satellites (~ 30) which transmit their position and time. With the combination of the signals (min. 4 satellites), a receiver could identify its own position through intersection methods. There are some GNSS in use and they partly transmit on the same frequency (see figure 3). There are GPS (USA), GLONASS (Russia), Compass (BeiDou) and Galileo (Europe – under construction). Each global navigation satellite system consists of 24 to 34 satellites in altitudes of 19,000 km till 25,000 km. The European system – Galileo, the only system that`s not under military control, is still under construction and competes with china`s system – Compass for the same frequency channels. The channels were configured for thin bandwidth, so that important military channels are not overlaid. SBAS is an additional system that makes use of geostationary satellites which have a transponder on board that broadcast on the same frequency channel as GPS correction signals for improving the positioning. The additional SBAS system with geostationary satellites for Europe is called EGNOS. There are several SBAS systems in use and intended, which are dispersed over the world and continents (see figure 4). There is the WAAS (Wide Area Augmentation System) from the United States, the MSAS (Multi-functional Satellite Augmentation System) from Japan, the proposed GAGAN (GPS-aided geo augmented navigation) from India, the proposed SDCM (System for Differential Correction and Monitoring) from Russia as well as some commercial solutions.
– The satellite ephemerides for GPS and GLONASS, – earth rotation parameters – IGS tracking station coordinates and speed measurements – GPS and IGS monitoring stations and their time information – The tropospheric zenith path delay – Global ionospheric maps (www.igs.org/components/prods.html) The IGS centers generate and provide accurate GPS and GLONASS products and facilitate support. The IGS service portal is called GGOS. GGOS integrates different geodetic techniques, different models and different approaches in order to ensure a long-term, precise monitoring of the geodetic observables. The benefit of low cost GNSS applications is brilliantly described and taken in focus in the targets and working groups of UNOOSA. The United Nations Office for Outer Space Affairs (UNOOSA) is the United Nation’s office responsible for promoting international cooperation in the peaceful use of outer space. UNOOSA serves as the secretariat for the General Assembly’s only committee dealing exclusively with international cooperation in the peaceful use of outer space (www.UNOOOSA unvienna.org). UNOOSA is the current secretariat of the International Committee on Global Navigation Satellite Systems (ICG). The current and future development planned GNSS and SBAS systems are described in one of the main ICG publications. Tablet-PC with GNSSApplication
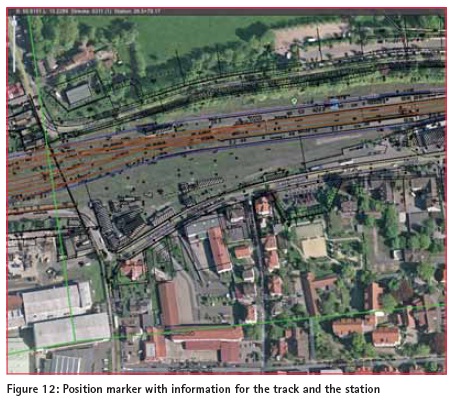
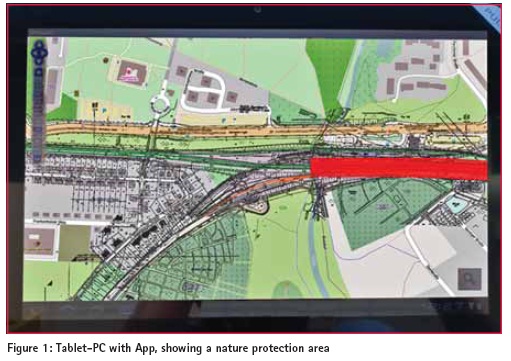
Subsequently, the data can be read out and committed to other computers for further editing or for documentation. It’s also possible to synchronize data via Internet or transferred to experts. The app is working on the android system (minimum version 3 – “Honeycomb”). The SD card space should be minimum 32 GB. When the app starts, the dataset is loaded and the internal GPS is on reception. Over the Bluetooth connection, an external GPS receiver can be connected. This has a tremendous infl uence in raising the accuracy of the positioning without using any mobile GPRS /3G /4G or internet services. FeaturesThe tablet shows your position in an information system background, so you can retrieve information and determine points of engineering maintenance interest (rail or electric wire faults). The system has a layered structure on which several datasets can be imported. Data of objects like bridges, tunnel, crossings, rail switches or nature protection areas are available as well as information about the whole rail net like the track numbers and the chainage.
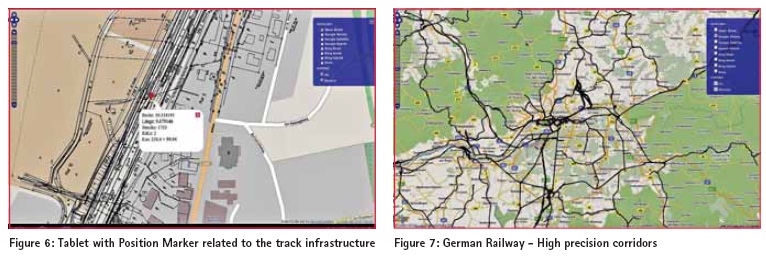
The position of the user is shown in the middle of the monitor as standard. In the upper menu console the coordinates are shown as well as information to the track the user is on. So there is shown the nearest track number and the chainage at this position. It also classified the rails in main or stationary rails and additionally could replay directional if there were nature protection areas to estimate. The tracked data can be exported to just save or use it for documentation purposes or for further processing. The High precision corridors are a combination of raster and vector data of the tracks and the track vicinity infrastructure. All this are stored on the SD card. The navigation tool allows the precise navigation based on geo position, track number and railway station ID. If the online use is not possible, the background for the geo position is the raster data of the railway cadaster. Additional markers can be loaded for representing clearance restrictions. Feature resume – Diverse basis layer – IVL drawings (infrastructure maps of the Deutsche Bahn AG) – Information of main and rail station tracks – Information of chainage – Search function to navigate to stations, tracks with chainage or coordinates – Display position with marker – Display clearance restrictions – Display environment protected areas – Set points of interest Components The Android unit with application and internal GNNS chip. Diverse information layer are also offl ine accessible because they are stored on the SD Card. An OEM GNSS (GPS/GLONASS L1) sensor plugged on via Bluetooth. ConclusionThe app is useful as a low cost GNSS solution for investigation, capturing measurements in real time and simple for field evaluation. Further analyzing subsequently on high end software is feasible. The app can be modified for other duties so it could be convenient for diverse disciplines. At the time, it is on the stadium of a pilot project and has to extend in its features. ReferencesIGS (www.igs.org/ components/prods.html) http://www.ggos-portal.org/ lang_en/GGOS-Portal/EN/GGOSProducts/ GGOS-Products.html SAPOS article and websites (www.sapos.de) Technet-rail (www.technet-rail.de) UN OOSA (www.oosa.unvienna.org/) EUPOS (www.eupos.org) ICG_ebook.pdf – Current and Planned Global and Regional Navigation Satellite Systems and Satellite-based Augmentations Systems
|

















 (9 votes, average: 2.11 out of 5)
(9 votes, average: 2.11 out of 5)




Leave your response!