| GNSS | |
GAGAN: Status and Update
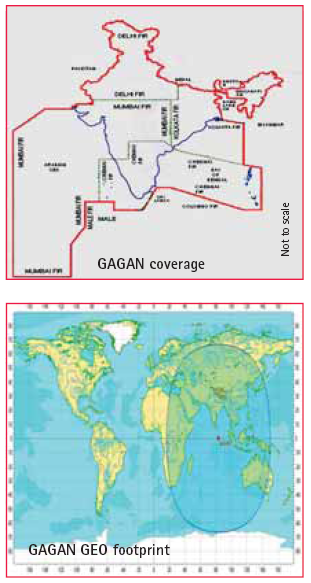
The GAGAN (GPS Aided Geo Augmented Navigation) system is a planned implementation of a Satellite Based Navigation System (SBAS) jointly developed by Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and Airports Authority of India (AAI), to deploy and certify an operational SBAS over Indian Flight Information Region. When commissioned for service, GAGAN will provide a civil aeronautical navigation signal consistent with International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) Standards and Recommended Practices (SARPS) as established by the GNSS Panel. ICAO endorsed GNSS as Future Air Navigation systems (FANS) for civil aviation.
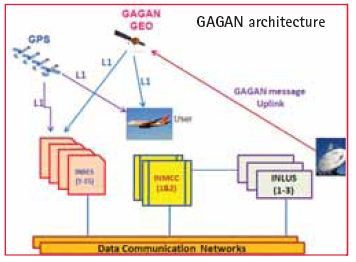
GPS satellites’ data is received and processed at widely dispersed Indian Reference Stations (INRESs), which are strategically located to provide coverage over the required service volume. Data is forwarded to the Indian Master Control Center (INMCC), which processes the data from multiple INRESs to determine the differential corrections and residual errors for each monitored GPS satellite and for each predetermined Ionospheric Grid Point (IGP). Information from the INMCC is sent to the INLUS and uplinked along with the GEO navigation message to the GAGAN GEO satellite. The GAGAN GEO satellite downlinks this data to the users via two L-band ranging signal frequencies (L1 and L5), with GPS-type modulation. Combination of Terrestrial and VSAT communication links are being established between INRES and INMCC sites as a back-bone network by AAI. An iono model called IGM-MLDF (ISRO GIVE Model-Multi Layer Data Fusion) developed by ISRO is incorporated in the INMCC operational software to represent the ionosphere variation, both spatial and temporal, over Indian region. On installation, integration and testing of the ground elements and integration with GSAT-8 GEO satellite, the GAGAN signal-in-space, available since December 2011, is for non-aviation users such as survey, geodynamics, road and rail applications, vehicle tracking, intelligent traffic systems, land management, scientific research and maritime applications, etc. The FSAT was completed during July 2012 and the GAGAN signal in space is evaluated using SBAS receivers at various locations across the country and the system performance was verified. SBAS user receivers were deployed at various locations within India, and the performance in terms of accuracy and integrity were monitored and were found to be within specifications. The second GEO satellite GSAT-10 will be launched in September 2012 and integrated with 2nd INLUS at Bengaluru. The third INLUS located at New Delhi, will serve as a redundant system to the 1st INLUS at Bengaluru for GSAT-8 GEO satellite. As the system is ready for certification by DGCA, the data from all the INRES are being collected and processed to study and analyze the occurrence of any HMI (Hazardously Misleading Information) in the user received signal. A Technical Review Team (TRT) has been formed by the DGCA to review the system performance in terms of integrity and other factors to be compliant with ICAO requirements.
|















 (3 votes, average: 3.33 out of 5)
(3 votes, average: 3.33 out of 5)




Leave your response!