| Mycoordinates | |
Rural infrastructure in India New thrust areas
|
||||
| Rural development may be defined as structural changes in the socio-economic situation to achieve improved living standard of low-income population residing in rural areas and making the process of their development self sustained. It includes economic development with close integration among various sections and sectors; and economic growth specifically directed to the rural poor. In fact, it requires area based development as well as beneficiary oriented programmes. That’s why rural development is one of the main and important tasks of development planning in India.
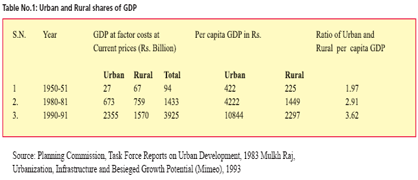
Development of rural areas is slow due to improper and inadequate provision of infrastructure with compare to urban areas. That’s why rural share in GDP is always less. The contribution of urban and rural shares of GDP can be illustrated in table 1. During 1990-91, the urban sector contribution in per capita GDP was 3.62 times more than the rural sector. The planning and development of human settlements and provision of required infrastructure are much better in urban areas. Rural population migrates near by Primate City due to more employment opportunities and better facilities. Similarly, the limited capacity of rural economy to accommodate the increasing population disregards the labour force as surplus to migrate large cities. Thus there is a need to encourage reverse migration to rural areas through proper development of rural infrastructure and basic amenities by creation of income generation avenues, improving the quality of life, etc. Rural infrastructure : New thrust areasRural infrastructure is not only a key component of rural development but also an important ingredient in ensuring any sustainable poverty reduction programme. The proper development of infrastructure in rural areas improves rural economy and quality of life. It promotes better productivity, increased agricultural incomes, adequate employment, etc. Bharat NirmanThe UPA Government has launched “ Bharat Nirman” time boundbusiness plan for action in rural infrastructure for next four years. Under Bharat Nirman, action is proposed in the following areas: • Irrigation • Rural Roads • Rural Housing • Rural Water Supply • Rural Electrifi cation • Rural Telecommunication Connectivity, etc. Bharat NirmanThe Task Ahead: The following bold targets are set to be achieved by 2009: i. To connect 66,800 habitations with population over 1000(over 500 in hill, tribal and desert areas) with all weather roads. ii. To construct 1,46,000Km of new rural roads iii. To upgrade and modernize 1,94,000Km of existing rural roads iv. Out of total investment of Rs. 1,74,000 crore envisaged under Bharat Nirman, investment on rural roads estimated at Rs. 48,000 crore. The Government has also decided to provide corpus of Rs. 8000 crore to Rural Infrastructure Development Fund (RIDF). Bharat Nirman through Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak YojanaRural connectivity is one of the major goals of Bharat Nirman. In India, there are more than 6 lakh villages located in different terrains e.g. plain, hilly, deserts, swamps, costal region, mountainous region, back water areas, tribal pockets, etc. The climatic condition also varies from place to place to a great extent. Due to improper planning, some villages are having multi road connection while others are deprived of even single road connection. In Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojna (PMGSY) has been decided to give one and only connection to each village. It is centrally sponsored programme with 100% financial assistance. All PMGSY roads are guaranteed defect free by the contractors for a period of 5 years and maintained by him under a contract. Funds for the maintenance contract are provided from the State Budget. After the period of 5 years, the roads will be transferred to the District Panchayat for further maintenance. PMGSY achievements can be summerised as follows: • 53,000 Km. of new rural roads constructed • 27,000 Km. of rural roads upgraded and modernized • 37,000 habitations provided all weather connectivity opening access for agricultural produce • Rs. 15,117 crore invested up to January 2006 • Monitoring the quality of road works through independent technical experts at the state and national level. Rural electrifi cationOut of the estimated 80,000 villages yet to be electrified, the 10th Five Year Plan (2002-2007) proposes to electrify 62,000 villages through grid supply. The remaining 18,000 remote villages are proposed to be electrified by 2011-2012 through the use of decentralized non- conventional source of energy. The rural electrification programme has beenincluded as a component of Pradhan Mantri Gramodaya Yojana(PMGY) and is being encouraged to pool resources from other schemes under Minimum Need Programme (MNP) and Rural Infrastructure Development Fund(RIDF) to meet objective of 100 % electrifi cation. A new scheme called Accelerated Rural Electrification Programme (AREP) has been launched. The participation of Decentralized Power Producers, PRIs, Rural Co-operatives, NGO, etc. will be encouraged. The Ministry of Power is pushing the concept of Rural Electricity Supply Companies (RESCOs) involving the private sector players by leasing out solar panel based light systems to village homes. The development and implementation of various rural infrastructure projects help to create values for the rural society. Similarly, involvement of Public as well as Private companies, NGO, etc. require the technical and managerial experts of engineering consultancy in rural areas. Bharat Nirman through Indira Awas YojanaIndira Awaas Yojana (IAY) targets rural families below poverty line who are either totally houseless or live in unserviceable kutcha houses. It is an effort to provide an identity and sense of security to rural poor households. Under the scheme, a maximum assistance of Rs. 25,000/- per house for plain areas and Rs. 27,500/- per house for hilly/difficult areas is given to BPL family to construct. Assistance is also provided for up gradation of kutcha houses @ Rs. 12,500/- per unit. . 60% of the houses are to be for SC/ST beneficiaries. Rural housing is one of the major goals of Bharat Nirman.The target of IAY in Bharat Nirman is as follows; • To construct 60 lakh houses over the next 4 years( 2006-2010) • Investment in Rural housing will be about Rs. 12, 000 crore IAY: Achievements:• Allocation for IAY has increasedfro Rs. 2750 crore( 2005-06) to Rs, 2920 crote( 2006-07). • About 9.6 lakh houses have been constructed so far in current year( 2005-06). • About 139 lakh houses have been constructed under IAY all over the country since inception of the scheme upto January 2006. • An amount of Rs. 25,500 crores have been invested so far in IAY. There is provision of free electricitry connection to be provided to IAY houses under Rajiv Ganghi Gram Vidutikaran Yojana. Planned urbanization with rural ambianceThe formation of cluster of rural settlements, which acts as a viable planning unit, is linked to the nearest towns then receives the needed growth impulses and makes it-self integrated with the town economy. It emphasizes the importance of urban infrastructure in rural areas. Based on it, Planned Urbanization with Rural Ambiances (PURA), as propagated by Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam, the President of India, in his vision 2020, argues the following connectivity for the cluster of villages: i. Physical Connectivity (roads, transport facilities, etc.) ii. Economic Connectivity (Banks, Commercial organizations, etc.) iii. Knowledge Connectivity (School, colleges, vocational education, etc.) iv. Societal Connectivity (Hospital, recreational facilities, place of worship, etc) and v. Electronic Connectivity (Phone, internet, cable, etc.) LocationThe location of PURA would be in the vicinity of a growing city and having high potential of development such as availability of local resources, skills, adequate water & power, good connectivity to transport networks, potential for employment generation, goods market, etc. |
||||
Pages: 1 2













 (2 votes, average: 3.50 out of 5)
(2 votes, average: 3.50 out of 5)



