| Surveying | |
Real time monitoring of Dalian Beida Bridge
|
Wang Jun, Yi Xiaodong, Wei Erhu
|
||||
|
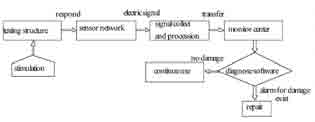
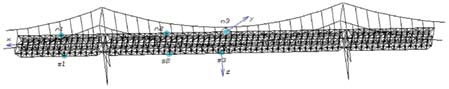
There are many traditional surveying methods used for the large-scale bridge structure deformation monitor such as the accelerometer measure, the total station surveying and the laser collimation, but these methods are limited by its function of which the continuity, timeliness and automaticity can not meet the need of the large-scale construction dynamic monitor. In recent years, with the GPS hardware and software technology developed, especially the GPS receiver with the high data-collection frequency (for example 10Hz even 20Hz[1][4]) appearanced as well as the GPS data processing was improvement, the GPS-RTK technology applied in large-scale bridge dynamic deformition monitor with real-time or quasi-realtime has become true[2][3]. Further, with the Fourier transformation tool the bridge base frequency could be obtained, the data of bridge vibrational state in spatial frame and frequency range distributed characteristic may provide the key to understand whether the bridge structure is health under the load drive environment. Structure health monitor flowchart [7] is shown in fig 1. Fig 1 Health monitor flowchart Fig 2 monitor points distribution Testing plan and processInstallment of GPS sensor antanaIn the bridge structure health examination, the sensor type, quantity and the structure testing position will guarantee the monitor effective implementation. Unsuitable sensor disposition would affect the precision of recognition parameter, one good sensor disposition plan aims to achieve: Testing process with GPS-RTKThe entire test had been implemented by TRIMBLE-5700 of the dual-frequency GPS receiver, S0, the GPS base station, located in spacious place nearby the bridge as seen in Fig 3 (a) where the error of multipath effect should be weaken, and rover station placed at s1, s2, s3, n1, n2, n3 separately, its main error source is the receiver system noise. The GPS receiver data sampling frequency was set 10HZ during testing process and data gathering time in each testing point will sustain more than 1h. Spatial distribution of dynamic deformation for bridge structureGenerally, with the external force (such as typhoon, earthquake and heavey-load car), the large-scale bridge vibration takes on simple harmonics nature, and its amplitude and frequency are changed too when the external force are changed, therefore, two kind of situations exists in the bridge dynamic deformation characteristic distribution . Where, A is an amplitude; f is a frequency; y is the deformation quantity; φ0 is the beginning phase; t is the time. Where, α is the coefficient of attenuation; Because along the direction of x and y axial, bridge vibration are smaller than that of z axial, therefore the structure vibration time interval curve obtained through computation is along the z axis. |
||||
|
Wang Jun, Yi Xiaodong, Wei Erhu
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
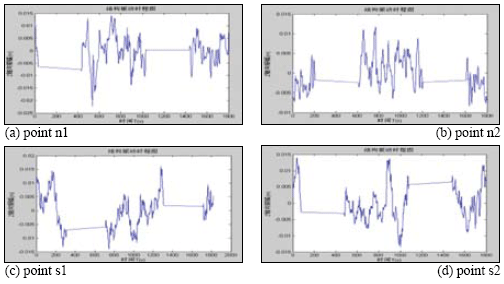
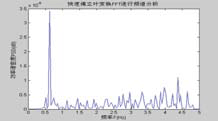
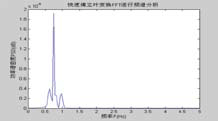
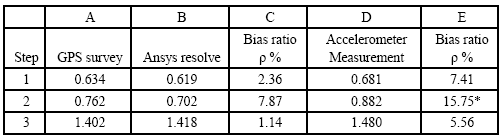
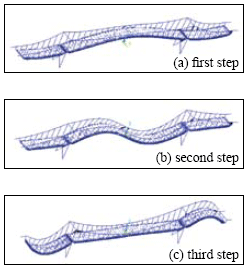
Testing point spectral analysis based on FFTBridge vibration frequency resolving in the condition of motivation contextBased on the motivation context, bridge vibration signal is not all the pure sine form[5]. According to the Fourier analysis, vibrating signal could be decomposed into many harmonic components. Fig 4 Time series of 4 testing points during same time-interval Fig 3 GPS device using in testing form[5]. According to the Fourier analysis, vibrating signal could be decomposed into many harmonic components. Actually, based on the time series, the (a) first step (b) second step (c) third step Fig.5 Power spectral density of bridge bridge vibrates frequency of fs in various steps harmonics could be decides by spectral analysis which are supported by measured waveform or the data come Tab.1 Comparison of vibration frequencies between GPS solution and other methods Fig 6 bridge various vibration types using finite element method from discrete processing. Formula (5) is the discrete form of Fourier transform. In Eq (5) Where cross direction express the frequency (Hz) vertical direction express the PSD (dB). Validity checking of GPS dynamic surveying techniqueDeterministic model method based on finite element Because the testing bridge has complete structural design material, in order to understand the feasibility of using the GPS dynamic surveying technique to get the bridge multistage vibration frequency. A deterministic model has been established to resolve the bridge vibration frequency caused by load with the finite element method. The software of finite element computation is Ansys. Accelerometer measurement methodIn the same point and same time, Accelerometer with the type of 891, which was produced by State Bureau of Seismology Engineering mechanics Research institute, had been set to obtain bridge vibration frequency, and the data processing software adopted Donghua data collection and processing system. It is shown from table 1 that the vibration mode deviation of bridge first three steps in same place is very small when comparing between the GPS surveying result and the accelerometer measurement as well as the result of using the Ansys finite element resolving. Every step data matchs well among them except the second step frequency value acquired by accelerometer is bigger. It is also known from the bridge testing that the accelerometer has been used in structure vibration test for its advantage of light weight, small volume and no affecting to testing system, but this method could make bigger measuring error than other’s and the deformation result is not direct-viewing too, when the structure oscillation is slow, it could not measure the structure of whole vibration amplitude. ConclusionThe vibration mode measured by GPS sensor receiver and accelerometer coincide with the result of using the finite element method, it indicates that the overall rigidity of the testing bridge structure conforms to the actual requirement From the view of testing analysis flow, the GPS-RTK method has the characteristic of simple operation, nimble and convenient; with the GPS receiver, it is easy to monitor the bridge of three dimensional dynamic deformation in real-time as well as first step bridge vibration mode frequency or higher step one which can provide the datum data directly for the bridge use, maintenance and condition evaluation. Reference:[1] J.J.Guo, L.J.Dai, Y.C.Lu, Study of the Humen bridge GPS(RTK) realtime displacement monitors Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2000.12:4-5. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Pages: 1 2

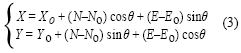


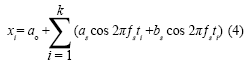
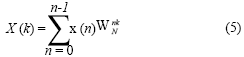













 (No Ratings Yet)
(No Ratings Yet)




