| Geodesy - New | |
Efficiency and geometric precision of Chinese spaceflight TT&C network observing Tiangong-1
In this paper, the efficiency and geometric precision (PDOP) of Chinese spaceflight TT&C network observing Tiangong-1 were calculated and analyzed based on ground-based TT&C network and the new TT&C network
|
 |
|
 |
|
China has invested enormous effort in manned space engineering. The Tiangong-1 and Shenzhou-8 have been launched, twice rendezvouses have been accomplished successfully. In order to meet the requirements of the manned space engineering on the TT&C network, and prepare for our country’s space station construction on TT&C in the future, two satellites of Tianlian-1 Tracking Data Relay Satellite System have been launched and are running together, and been used for the rendezvous task.
China’s existing TT& C Network is composed by five control centers, number of Ground-based control stations/ships, and two tracking and data relay satellites. The TT&C system is the unified S-band system which is widely used in international, so we could use other country’s TT&C stations on the task requirement to expand the range that can be observed.
This paper will analyze the coverage efficiency and geometric precision based on Ground-based TT&C Network and the new TT&C Network included Tianlian-1 Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System respectively according to the Tiangong-1 task.
The research present that the coverage efficiency of our country’s new TT&C Network included Tianlian-1 Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System has met the manned space engineering requirement. The coverage efficiency has improved several times compared to the traditional Ground-based TT&C Network, and the Tiangong-1 can be totally controlled when located in our country and nearby. On the geometric precision, the PDOP of the new TT&C Network include Tianlian-1 system observe Tiangong-1 can be less than 50 in most time, and it’s benefit for the rendezvous task and determining the orbit and operating status after the Tiangong-1 and Shenzhou-8 docked. Integrated USB ranging accuracy and PDOP values calculated results, consider of the orbit determination needs and only consider the impact of ranging accuracy the positioning accuracy of our country’s TT&C Network observing Tiangong-1 can be better than 10m in most time, and can be better than 20m almost all the time.
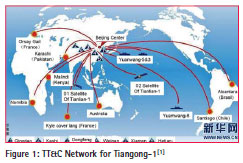
The TT&C network for Tiangong-1
It’s the first time that the TT&C Network for Tiangong-1 used for manned spacefl ight task after the Tianlian-1 system was completed. The TT&C Network must have high coverage efficiency, accuracy and reliable because of the rendezvous and docking, and another rendezvous and docking after separate. The TT&C Network for Tiangong-1 is composed of Beijing spaceflight control center, six domestic land-based stations, eight foreign land-based stations, three Yuanwang measurement ships, and Tianliang-1 tracking and data relay satellite system, the measurement ships will maneuver according to mission requirements.
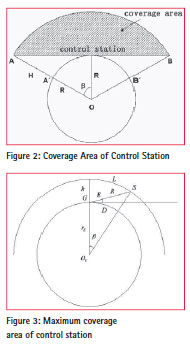
Coverage and PDOP calculate method
Coverage area of control station
The coverage area of a control station for the spacecraft with the orbit altitude H was the shadow area shown in figure 2. Projected onto the sphere is an arc area, and the control station is the center, the radius is the long from the control station to A`or B`[2].
In order to improve the data quality and reduce affections of atmospheric refraction of electromagnetic wave propagation, the minimum elevation angle must be set. For the observing of near-earth spacecraft, the spacecraft orbit can be seen round and the earth is stationary.
Figure 3 shows the coverage area when the spacecraft through control station zenith.
Coverage area of TDRS
The tracking and data relay satellite is a geosynchronous satellite, assume the satellite location is (ηS, 0). The designed antenna angel is decided by the tracked spacecraft apogee altitude ha, see equation (1).

PDOP calculate method
Now the common measure systems used by our county’s TT&C Network are single station RAE and multi stations ranging system, and we derivative the PDOP calculate method based on multi stations ranging system.

In order to briefly discuss, we only considered the ranging error, and didn’t consider other affections of measurement errors. Assume the distance measurement values at the time t are Ri (i=1,2,3), M (X,Y,Z), is the location of spacecraft at the time t in the geodetic coordinate system, three stations locations are S1(X1,Y1,Z1), S2(X2,Y2,Z2) and S3(X3,Y3,Z3) in the geodetic coordinate system,
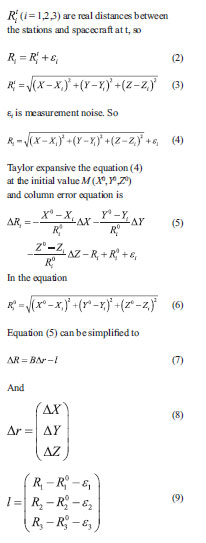

Coverage analysis
The orbit data of Tiangong-1 and Tianlian-1 used in this paper were two-line element set (TLE) data that published by North American Aerospace Defence Command (NORAD), the ephemeris data will be updated from time to time according to demand. The TLE data is a kind of general ephemeris data and founded by NORAD.
The orbit altitude of Tiangong-1 is nearby 330km, the coverage efficiency of the TT&C Network to the 330km high will be analyzed first, then the coverage efficiency of the TT&C Network to Tiangong-1 will be analyzed, at last the affection of Tianlian-1 to the TT&C Network will be analyzed.
One day ephemeris data of Tiangong-1 from 2011.10.2 00:00:00.00 to 2011.10.3 00:00:00.00 was choice to calculate when Tiangong-1 was in the test orbit, the ephemeris data of Tianlian-1 was also in that period. The minimum elevation angel was 5o, and the duration time of the station must be longer than 360s.
Coverage efficiency analysis of ground-based network
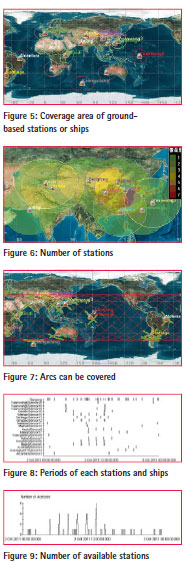
Figure 5 presents the area that can be covered by ground-based stations or ships, figure 6 presents the area that can be covered by multi groundbased stations or ships and the number of the stations or ships.
The area that can be covered by multi ground-based stations or ships is very small according to figure 6, only some areas in our country can be covered by multi ground-based stations, the max number of stations that can cover the same area is six. Through statistical, the area where can be covered is 17.9% the total.
Figure 7 presents the arcs that Tiangong-1 can be controlled, figure 8 presents the periods of each stations or ships when available, figure 9 presents the change of the number of available stations or ships from time to time. Table 1 and table 2 present the statistics result of the arcs can be controlled.
The arc period use single station is short. When only use groundbased TT&C Network, the total time observing Tiangong-1 is short and is only 18.77% a day.
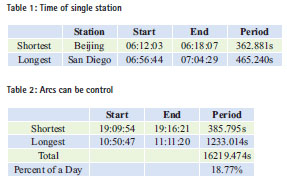
Coverage efficiency of the new TT&C network
Figure 10 presents the areas where can be covered by the new TT&C Network, the pink is the area covered by Tianlian-1 01, the blue is the area covered by Tianlian-1 02. Figure 11 presents the areas can be covered by multi stations, ships and satellites, and the number of stations, ships and satellites.
Figure 11 presents the areas where can be covered by multi stations, ships and satellites have been improved, only some area in Pacific Ocean and South American, and east of North American can’t be covered, the max number of stations that can cover the same area is eight. Through statistical, the area where can be covered is 88.21% the total.
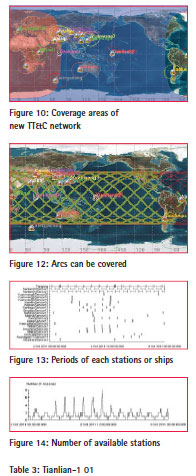
Figure 12 presents the arcs that Tiangong-1 can be controlled, figure 13 presents the periods of each stations or ships when available, figure 14 presents the change of the number of available stations or ships from time to time. Table 3 and table 4 present the period when Tianlian-1 01 and Tianlian-1 02 can cover Tiangong-1.
From table 3 and table 4 we can conclude the effect of Tianlian-1 observing Tiangong-1, the total time that single satellite can observing Tiangong-1 account over 55% a day.
Jiang hu had analyzed relay performance of Tianlian-1 01 in the paper [3], he pointed out that the shortest period that Tianlian-1 01 can cover the satellite with 400km altitude and 400 inclination was 1357s, the longest period was 3510s, and the total time account 56.5% a day. So this paper’s result is in keeping with that. Table 5 presents the statistics result of the sustainable arcs that the new TT&C Network can cover Tiangogn-1.
It can be concluded that the total time account to 86.37% a day, and more than 4 times than 18.77% which only use ground-based TT&C Network. The demanded coverage efficiency of the TT&C Network for manned spacefl ight is: there must be more than 9min one loop evenly that the spacecraft can be controlled when it is in task orbit, and won’t be more than one loop when control stations couldn’t communicate with the spacecraft. It’s 17.2min one loop evenly when only use ground-based TT&C Network, and control stations can communicate with the spacecraft all the loops; and 79.0min one loop evenly when only use the new TT&C Network, and control stations can communicate with the spacecraft all the loops. So using our country’s new TT&C Network can improve the period when spacecraft can be covered effectively, and can guarantee Tiangong-1 task implement smoothly.

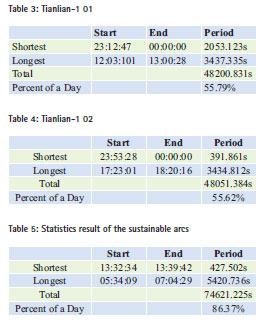
PDOP analysis
The geometric precision based on Ground-based TT&C Network and the new TT&C Network will be analyzed respectively in this part. According to the international TT&C standards, the spacecraft’s measurement position accuracy should be better than 100m, now the ranging accuracy of our country’s USB system is better than 2m, so the PDOP should be lower than 50.
The PDOP of the TT&C Network to the 330km high will be analyzed first, then the PDOP of the TT&C Network to Tiangong-1 will be analyzed, at last the position accuracy of the new TT&C Network observing Tiangong-1 will be concluded. One day ephemeris data of Tiangong-1 from 2011.10.31 00:00:00.00 to 2011.11.1 00:00:00.00 was choice to calculate when Tiangong-1 was in the rendezvous and docking state of readiness orbit, the ephemeris data of Tianlian-1 was also in that period. The located of the stations and ships were the same as they were in the coverage efficiency analysis, and the minimum elevation angel was 5o.
PDOP of Ground-Based TT&C Network
Figure 15 presents the PDOP of 330km altitude all over the world, the color in the area represent the change of PDOP. It can be concluded that the areas can be covered by multi stations and ships are small when only use ground-based TT&C Network, where are central and eastern areas, and some areas of Xinjiang and Tibet of China, and some areas in West Asia and Western Pacific in some areas, the total areas account to 2.26% all the world.
Figure 16 presents the result of observing Tiangogn-1, the pink is where PDOP is greater than 60 or unavailable, and figure 17 presents the change of PDOP from time to time a day when groundbased TT&C Network observing Tiangong-1. After statistics obtained, the time is 68min that there are at least 3 stations and ships can cover Tiangong-1 at the same time a day, and it account 4.74% a day, and the minimum PDOP is 1.98, the maximum is 105.68.
After statistics obtained, the longest period is 534.67s and the shortest period is 23.66s when Tiangong-1 can be covered by at least 3 stations and ships.
PDOP of the New TT&C Neteork
Figure 18 presents the PDOP of 330km altitude all over the world, the color in the area represent the change of PDOP. It can be concluded that the areas can be covered by at least 3 stations and ships are almost 4 times than that when only using ground-based TT&C Network, where are in addition to the northeast of Heilongjiang province in China a outside of almost all land areas and most parts of Central and West Asia, and some areas in Western Australia and South Atlantic, continental and marine areas, the total area account to 8.31% all the world.
Figure 19 presents the result of observing Tiangogn-1, the pink is where PDOP is greater than 60 or unavailable, and figure 20 presents the change of PDOP from time to time a day when the hew TT&C Network observing Tiangong-1. After statistics obtained, the time is 176min that there are at least 3 stations and ships can cover Tiangong-1 at the same time a day, and it account 12.20% a day, and it is almost 3 times than that when only using ground-based TT&C Network. The minimum PDOP is 1.32, the maximum is 1000.00.
In view of the situation that PDOP is great and the maxima is greater in few areas, we analyzed the position of Tiangong-1 and other situations and concluded that after Tianlian-1 added to the TT&C Network, when the spacecraft located in some positions, uneven distribution of stations on the perpendicular to the direction of the orbital plane, and this led to the PDOP larger. And some areas become available after Tianlian-1 added to the TT&C Network also led to the PDOP larger.
Position accuracy of the new TT&C network observing Tiangong-1
Doing statistics of PDOP less than 50 regional worldwide, the result is presented in table 6. It can be concluded that almost all areas PDOP is less than 50, and account 97.21% the area available, 8.08% all over the world.
After the statistics of the sub-arc of observation Tiangong-1, the maximum PDOP is 48.24, and the minimum is 1.32. The maximum average PDOP of a single arc is 13.80, and the minimum is 2.13. The average PDOP a day is 5.54.
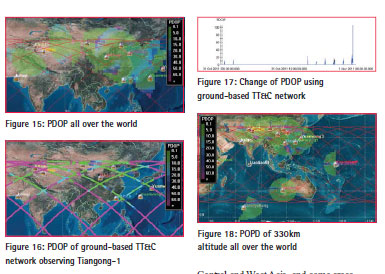
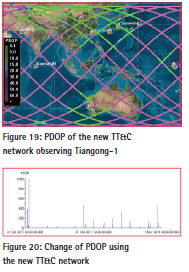
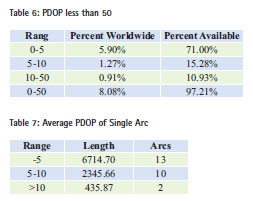
Table 7 presents the average PDOP statistic result of each single arc. When using the new TT&C Network, there are 13 arcs that the average PDOP is less than 5, 10 arcs that the average PDOP is between 5 and 10, only 2 arcs that the average PDOP is great than 10.
According to our country USB system ranging accuracy and the simulation result of PDOP, it can be concluded that if only consider the ranging accuracy, the position accuracy of our country TT&C Network observing Tiangong-1 can be better than 10m in most time, and better than 20m in almost all the time.
Conclusion
The conclusion is obtained according to analyzing the coverage efficiency:
(1) When only using the ground-based TT&C Network, the shortest period is 362.881s of a single station, and the longest is 465.240s; the shortest length of the arc can be controlled is 385.795s, and the longest is 1233.014s; the total time is 16219.474s a day, and account 18.77% a day;
(2) After the entry of Tianlian-1, the shortest length of the arc can be controlled is 427.502s, and the longest is 5420.736s; the total time is 74621.225s a day, and account 86.37% a day;
The conclusion is obtained according to analyzing the PDOP of the TT&C Network observing Tiangong-1:
(1) When only using the ground-based TT&C Network, the areas where can be covered by multi stations and ships are small, account 2.26% worldwide. The time is 68min that there are at least 3 stations and ships can cover Tiangong-1 at the same time, and it account 4.74% a day, and the minimum PDOP is 1.98, the maximum is 105.68.
(2) When using the new TT&C Network, the areas can be covered by at least 3 stations and ships are almost 4 times than that when only using ground-based TT&C Network. The time is 176min that there are at least 3 stations and ships can cover Tiangong-1 at the same time a day, and it account 12.20% a day, and it is almost 3 times than that when only using ground-based TT&C Network. The minimum PDOP is 1.32, the maximum is 1000.00. According to our country USB system ranging accuracy and the simulation result of PDOP, it can be concluded that if only consider the ranging accuracy, the position accuracy of our country TT&C Network observing Tiangong-1 can be better than 10m in most time, and better than 20m in almost all the time.
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the national ‘863 Project’ of China (No. 2008AA12Z308) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 40974003).
References
[1] XINHUANEWS. The TT&C network for Tiangong-1 and Shenzhou-8 rendezvous and docking[EB/OL]. [2011-9-29]. http://news.xinhuanet.com/ mil/2011-09/29/c_122108714.htm.
[2] Wei erhu. Research on the Designment of Chinese Space LVBI System and Computation[D]. Wuhan University, 2006.
[3] Jiang hu. Analysis of Relay Capabilities for First Sino-TDRS Satellite[J]. GNSS Word of China, 2008(6):25-26.
[4] CHINA NEWS. “Shenzhou” orbit determination accuracy has met one hundred meters orders of magnitude and into the world advanced level [EB/OL]. http://www.chinanews. com/2002-11-13/26/243201.html.
[5] Li zhigang, Qiao rongchuan, Feng chugang, ect. USB and pseudocode spread spectrum technology joint determination of satellite orbit: Aerospace Measurement and Control Technology Symposium 2006, Xining, 2006[C].
[6] Hao yan. Spacefl ight TT&C Network[M]. Beijing: National Defence Industry Press, 2004.
[7] Chen yiyuan, Yin liming, ect. Satellite radio monitoring and control technology (II) [M]. Bejing: China Astronautic Publishing House, 2007.
[8] Vick C P, Berman S D, Lindborg C. Tracking and Data Relay Satelli-te System (TDRSS)[EB/OL]. [1997- 4-15]. http://www.fas.org/spp/ military/program/com/tdrss.htm.
[9] Wang qi, Yang ying. STK in the computer simulation [M]. Beijing: National Defence Industry Press, 2005.












 (5 votes, average: 2.20 out of 5)
(5 votes, average: 2.20 out of 5)




Leave your response!