| Mapping | |
With e-Services towards transparent and trustworthy cadastre
The paper presents an overview of developments of e-services which are available in the Czech Republic in order to provide accessible cadastral data to any customer of a cadastral offi ce |
 |
|
 |
|
Information has generally been one of the most precious goods in recent decades. It is possible to buy and sell it, to barter it or just only freely provide it. The value of the information itself is very often based on the fact that it is more valuable when the actual information is less accessible and more desired. Yet some of the information and its timely acquisition or providing may be crucial for conserving resources or rescuing material values, health or human and animal lives.
We have been witnessing an unprecedented growth in the number of demands for spatial data recorded on the territory in recent years. Information about properties and their owners and users is absolutely necessary for effective functioning of a real estate market, strategic decision making processes, environmental protection or other important human activities in the area. Access to cadastral information is not only important for public authorities or companies that deal in some way with real estate, but in many life situations it is very important for individuals as well. The principle of cadastral publicity can ensure equal access to information for all groups of stakeholders.
Principle of publicity
Public cadastre is connected with the principle of formal and material publicity (a principle of public trust). The principle of public cadastre in the Czech Republic states that the Cadastre of Real Estate is public and everybody is entitled to consult it, make copies, extracts and sketches for their need or obtain data from the collection of documents stored in document funds. When this principle was laid down in the new cadastral law at the beginning of the 1990s, legislators had in their mind primarily a visit to the cadastral office in office hours by a client who personally demanded required data at the information desk. With the development of information and communication technologies the principle of publicity and the right to obtain information from the cadastre is mainly based on easy access to the required information through the Internet and mobile applications. Authors of this paper want to present which historical and legislative reasons led the Czech society to a relatively liberal approach in this matter, what information can be obtained from the Czech cadastre and how it can be obtained.
Principle of Public Cadastre in Historical Context
The principle has been applied on the territory of Czech lands almost continuously since 1871, it means 145 years. The only time when the principle was slightly weakened, the period from 1964 to 1992, the law required an applicant to demonstrate a legitimate interest for consulting the real estate records or issuing extracts from the registry. However the usual practice in this period usually was such that the extracts from the registry were issued without any formal verification of the interest legitimacy in these data. In 1871, when the protection of confidence in the records on land rights kept in the Land Book was enshrined, the principle of formal publicity was significantly enhanced in the legal system of the Austrian tradition. By comparing systems of land registration in other European countries, which are based on different principles, we can demonstrate that the system providing a high degree of property rights protection, especially of buyers and mortgage lenders, always includes a widely understood principle of public land records, especially data on the property rights and defects encumbering the property. The Czech Republic is one of the countries with the Austrian tradition of land law originally based on the Common Civil Code from 1811.

Principle of Public Cadastre in European Context
Land Registries in European countries can be divided into three basic groups in terms of access to the contents of the register and issuing extracts and copies:
– “Austrian” group, which includes Austria, a northern province in Italy, Hungary, the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Poland, Slovenia, Croatia and other countries in the former Yugoslavia. This group of countries is characterized by very broadly interpreted principle of public data records, including land rights to real estate. Easy access to these data is also traditional in the Nordic countries, so they can be assigned to this group as well.
– Germany and Switzerland, where the access to the land register requires proving the legitimate interest. Without fulfilling this obligation only contact information on the registered owner of a particular parcel is available. Only notaries who draw up all real estate contracts and secure information for a specific real estate purchase contract are exempt from the obligation to demonstrate the legitimate interest.
– France, Spain, England, where legislation does not enable direct access to the land registry and written information can be provided whilst an approval of the registered owner with providing specific information may be required.
Outside Europe, the publicity principle is broadly applied e.g. in Canada and Australia, although their systems of land registration are often quite different from the Czech cadastre. Contracts on real estate are registered in these systems and it is permitted to consult these contracts.
It is necessary to mention that the extent of publicity of a land registration system relates with the whole real estate trade of each country and with the level of state guarantees for persons who work on the assumption of rightness of the land register. For example, in systems where every real estate contract is mediated by a notary, the notary´s access to land records is sufficient enough. For other purposes (real estate services, preparation for construction of public utility buildings etc.) being able to contact the registered owner is satisfactory as well.
Application of Publicity Principle in Czech Cadastre of Real Estate
The provision of data from the Czech cadastre is not totally unlimited. It is impossible to obtain a summary of ownership of a specific owner from all over the Czech Republic or given territorial area by simple consulting these data. The same applies to the collection of documents and real estate prices. The provision of data from the collection of documents is carried out by providing a certificated or simple copy. Only the person, who proves their identity and states the purpose for which the data are requested, can obtain the data. Cadastral offices keep records of persons who have demanded the data for a potential inspection by the Office for Personal Data Protection.
In systems that are very liberal, which is the contemporary one in the Czech Republic, any restriction of the cadastral publicity would bring great difficulties. The opportunity to get full information from the cadastral register on legal relations independently on a real estate owner enables buyers and pledgees to take fully into consideration major risks of a particular real estate transaction. It is also necessary to conserve the public collection of documents, on the basis of which registrations were carried out. It reduces the risk of fraud in real estate transactions. The public cadastre also enables to determine whether debtors own some properties. To satisfy outstanding claims creditor can suggest for example seizure of property. That is precisely how the new procedures in the implementation of a property seizure have contributed to greater discipline of debtors in debt payments in recent years. Proposals for a seizure of immovable property are registered in cadastre to the debtors and thus generally relate to all of their property. They are registered immediately, usually the same day or the day after delivering. So, decisive factors for completion of real estate transactions can be changed virtually overnight. That is why it is important not only to conserve cadastral publicity, but also enable the information access remotely via the Internet, so that the important data can be examined immediately before signing a contract.
The publicity of the Cadastre of Real Estate of the Czech Republic is not in confl ict with the protection of personal data. The Law on Personal Data Protection explicitly counts on public registers such as the cadastre and also specifies how to handle the personal data that are included in such a public list. According to the law these personal data kept in a public list are considered as published.
The cadastre is a source of information that serves to protect property rights, for the purposes of taxes, fees and other financial fulfillments, to protect the environment, mineral resources, for protection of interests of state monument care, for territorial development, real estate valuation, scientific purposes, economic and statistical information and the creation of other systems. A broad concept of the public cadastre is necessary to fulfill above formulated purposes.
Ways of providing cadastral data
Cadastral authorities provide cadastral information to the public in several forms:
1. verbal form,
2. analogue form
▪ printed form,
▪ copies of deeds, owner’s folios/ excerpt from the cadastre, cadastral maps, identification of parcels,
3. digital form
▪ copies of deeds, excerpt from the cadastre, cadastral maps (PDF/HTML),
▪ textual and graphic computer files (exchange format),
▪ web sites,
▪ notifications.
In the past the most common way to provide outputs (information, excerpts, duplicates and copies) from cadastre was a handover at individual cadastral branch offices. The reason of that situation was the fact that only cadastral offices had access to the data from their territorial scope of activity and because a large among of data (contracts, deeds, measurements …) was only in analogue form.
The changes have started since 1992. Systematic management of cadastral data has been launched in an information system and was supported by digitalisation descriptive data (completed in 2000) and by digitalisation of geodetic data/ cadastral maps (1995 – 2017).
Electronic management of cadastral data continued in 2001 by creation a new Information System of Real Estates which included a joint management of descriptive data and geospatial information in one system and their continuous transport into a central database.
Electronic services of the cadastre of real estate
Some e-Services have been launched in the area of the cadastre of real estate, which enable to get a wide range of information from the cadastre for our customers. There are both free of charge services enabling to get some chosen data without any restrictions, as well as paid services providing verified documents serving as public documents, that is from the whole territory of the Czech Republic. Except for this, some other applications are for disposal facilitating the access to cadastral data and communication of inhabitants with cadastral offices.
Since 2013 there has been a legal obligation to submit the entry proposal on the form. The objective of this measure is to reduce errors that still occurred in the proposals for entry of right and get clearly formulated requirements for what should be registered into the cadastre of real estate according to the attached documents. In order to facilitate completing the form to the applicants a web application was launched enabling creation of the entry proposal in an interactive way. This application is interconnected to the cadastral database and draws some data from it. It leads the user through the entire process, and contains also some pre-prepared simplified scenarios for the most common situations. The application is very popular; in 2014 more than 629 thousands entry proposals were created via it. Since January 2014 it is possible not only to complete the entry proposal in electronic form but also to perform the registration into the cadastre of real estate on the basis of documents in electronic form. If the document is drawn up in electronic form, it must be provided with a qualified time stamp as well.
Thanks to the new Information System of Real Estates a first version of Remote Access to the Cadastre of Real Estate was launched in 2001. The Remote Access is a paid service enabling on-line access to the cadastre data via two options – a web application or web services (since 2005). The outputs are in digital form fitted with certified electronic signature.
To use the Remote Access application is necessary to have a user account. There are three types of user accounts – Ordinary accounts, Accounts for free Remote Access and Accounts for the purpose of issuing of authorized outputs from cadastre. The third one can be set up solely for subjects legally authorized for authorization of outputs from information systems of state administration (municipal authorities, notaries, Czech Post and Chamber of Commerce) and it enables to expand places where is possible to obtain outputs from Cadastre in analogue form.
From the beginning of 2004 was launched a web application Consultation of the Cadastre of Real Estate with limited range of digital information, without formalized outputs, nonauthorized but for free. The main reason to open this application was to tear down barriers between citizen and administration power and to publish detailed information about phase of procedures concerning requests for entry or record into the Cadastre. In the first instance there were only descriptive data that were followed by digital maps in 2008.
The latest news in a manner of provision of data is Service for monitoring of changes which was launched in 2014. This Service is based on communication by SMS, e-mail, data box or web services and follows changes on real estates and delivers short notifications. This is the first proactive utility for owners and associated persons to enable keep an eye on their own interests.
On-line applications for provision of data
Consultation of the Cadastre of Real Estate
The application has been operated since 1st January 2004. It is free to use, free of charge. From that time there were a lot of new versions with added features. The basic available information is about a real estate, cadastral procedures and cadastral maps. Descriptive data are usually updated daily; cadastral maps are updated up to their format – a vector format hourly, a raster format on demand.
Consultation of the Cadastre of Real Estate is the most frequently visited Czech governmental web page with average monthly visit 1.9 mil. Its content contributes to put the work of Cadastral Offices under permanent public watch and contributes thus to their transparency as well. That is the way the users have access to currently updated complex information from the cadastre of real estate directly from their worktable.
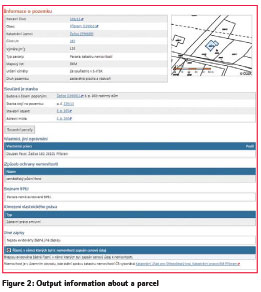
Information about a Real Estate
In this section there are available data about parcels, buildings, flats and non-residential spaces and building rights registered in the Cadastre. The information can be obtained by inserting the proper identification parameters of the property of interest.
The outputs consists of universally data as a unique identification and technical characteristics of the property, a name of owner/co-owners with postal addresses and respective shares, rights concerned the property or an information about ongoing legal changes (reference to the number of procedure – if any).
The basic information is displayed on web browser and contains many links to the additive details. If the user has an interest into, he can display the property on the cadastral map, find out all properties of the current owner, find out neighbouring parcels and theirs owners or get know if there is any price written in Cadastre for the property.
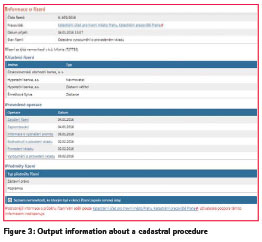
Information about Cadastral Procedures
In this section it is possible to get the detailed information about the progress of entry, record, note or confirmation of survey sketch procedures into the Cadastre. According to the number of procedure and the name of proper Cadastral Office you can see the date of delivery, current state of progress (e.g. commenced, stopped, rejected, new record prepared and approved, decided, dispatched, closed). There are also names of participants in the procedure, list of procedural acts carried out with date and information about the type procedure (e.g. ownership rights, mortgage).
By inserting the number of a procedure it is possible to obtain also the information on nearest 40 procedures (20 before a 20 after) with date of delivery and state of their progress. In this way you can follow the sequence of handling of your particular case. You can also get information about all the petitions delivered the same day by inserting the date of delivery. (1)
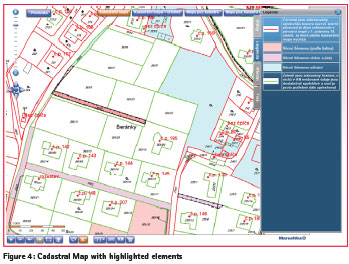
Cadastral Maps
In this section it is possible to display cadastral map all over the Czech Republic. Currently there is less than 10 % of territory without cadastral map in a vector format available; there are used original maps in a raster format with definition point of parcels in these areas.
Besides a general map viewing you can search parcels and buildings, display the quality of the measurement of boundaries (redbad/ green-good boundaries) or display easement to the property (blue/pink/orange coloured area).
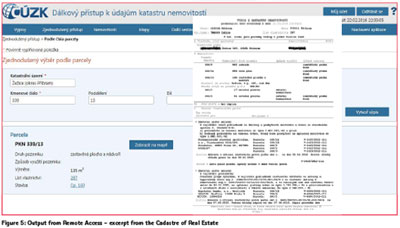
Remote Access to the Cadastre of Real Estate
The application was launched in 2001 and it is still getting improved. The last year its users interface was completely redefined into a modern design.
Remote Access enables to get data from the Cadastre at the whole territory of the Czech Republic. However, this is valid solely for the text outputs:
• Excerpt from the Cadastre of Real Estate
• Information about Parcels
• Information about Flats and Nonresidential Premises (Units)
• Ownership Overview
• Existence of Rights for a Person
• Course of Proceeding
• Depiction of Overview and Cadastral Map
• Copy of the Cadastral Map in PDF …and other Special Outputs
Cadastral maps in digital form are not for disposal over the whole territory. In areas without digitized cadastral map the raster picture of the cadastral map is for disposal.
Outputs from the Cadastre acquired in this way (e.g. Excerpt from the Cadastre) are both formally and factually identical with the documents issued by the cadastral office. Certified electronic signature is embedded in the outputs. Data provided via Remote Access can be considered completely updated because all changes of internal central database are transferred in 20 minutes interval to the Remote Access database as a rule. The Remote Access allows providing historic outputs as well; it means it allows generating outputs that have the same content like as those, that were done on a historical day.
The Remote Access was designed for registered customers, what can be almost anyone – real physical person or legal person. The procedure of gaining the access to the Remote Access includes only fulfilling an application form and proving the identity. This is necessary for guarantee of a payment and to be able to declare which outcome was created by whom Web Services of the Remote Access to the Cadastre of Real Estate
Web Services of the Remote Access is the separate part of the Remote Access application with the programme interface for access to cadastral data. Application enables connection of information systems of single users to this interface and via it utilization of cadastral data. Web Services provide data in the PDF or XML format and the scope is:
• Excerpt from the Cadastre of Real Estate
• Information about Parcels
• Information about Buildings
• Information about Flats and Nonresidential Premises (Units)
• Information about Building Rights
• Ownership Overview
• Existence of Rights for a Person
• Course of Proceeding
• List of coordinates of definition points (approximate centre of building or parcel)
Web Services application is charged and can be used solely by the registered users. The way to be registered is the same as in Remote Access, only the created account has to be different. The outcomes in PDF format are authorized by electronic signature.
Payment Portal
Payment portal allows anyone to obtain selected authorized digital outputs without having a user account. It is focused on customers that immediately need an authorized output and are able to pay for it online by credit card. Payment portal is an element combining the Consultation of the Cadastre and the Remote Access to the Cadastre. The interested person selects data and type of output via the Consultation of the Cadastre and the output is done by Remote Access to the Cadastre. Before downloading the output has to be done payment via secured Payment Portal. There is possibility to choose between following types of outputs:
• Excerpt from the Cadastre of Real Estate
• Information about Parcels
• Copy of the Cadastral Map in PDF
Monitoring of Changes in the Cadastre of Real Estate
The Service for monitoring of changes in cadastral data is provided to those persons who have real right to particular real estate or to participants of proceeding about such a right. It can be:
• the Owner,
• the Pledgee or Subpledgee,
• Easement Beneficiary,
• Pre-emptive right Beneficiary in case it is stipulated as material right,
• Beneficiary of the Right to purchase back, Right of better purchaser, Leaseholder or Tenant.
The service automatically informs the user about the fact, that there occurred a change in the Cadastre regarding the monitored real estate. The change means:
• Notice marking that the rights to real estate are affected by a change,
• Entry performance,
• Record performance,
• Note registration.
Messages of the Service for monitoring changes are informing about the change of data connected to the property. The messages are being sent at the latest within 24 hours after the monitored incident occurs.
Information about changes can be sent as a notification via Data box, e-mail or SMS or via web services in XML format. The service is charged and can be used solely on demand of the authorized person.
Conclusion
Information about real estate and property rights to them is needed for proper functioning of public administration and a real estate market. All above mentioned cadastral electronic services significantly contribute to the ease of obtaining the required information, to more efficient electronic communication in matters of registration of rights in the cadastre and to increase the security of real estate transactions. The whole process of computerization of the cadastre is the result of long-term conceptual steps that reduce costs and allow satisfaction of the increasing demand for cadastral information.
References
1) Ivan Pesl, Jiri Rydval and Vaclav Slaboch: Free Internet Access to Cadastral Data – First Experience in the Czech Republic, FIG Working Week 2004, Athens, Greece, May 22-27, 2004
2) Czech Office for Surveying, Mapping and Cadastre: Annual Report 2014
3) Veronika Nedvedova: Publicity of Cadastre of Real Estate, 2005
4) www.cuzk.cz
The paper was presented at FIG Week 2016, Christchurch, New Zealand, 2-6 May, 2016











 (No Ratings Yet)
(No Ratings Yet)





Leave your response!