| Applications | |
Cadastral reform project in South Korea
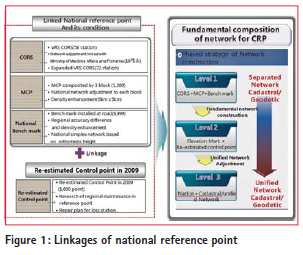
In order to solve the underlying problem, Korea MOLIT (Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport) enacted a special act on cadastral resurvey, proclaimed this on 16 September 2011. With the implementation of this special act from 17 March 2012, a CRP (Cadastral Renovation Project) has been being promoted in earnest. Therefore, a multipurposed control network should be firstly constructed to promote effectively on the CRP. The system of reference point for CRP has to be promoted by applying unified network of reference point based on the WGRS (World Geodetic Reference System) rather than applying by dual-reference points through surveying and cadastral surveying. MOLIT has performed a demonstration project for Digital Cadastral Construction from May 2008 to the end of 2012 for introducing the WGRS to the field of cadastral surveying and promotion of CRP. As a result of this project, in 2009, satisfactory 1600 reference points which have the accessibility, availability, good line of sight (sky-visibility) among cadastral triangulation point and cadastral control points distributed in nationwide were selected to maintain the cadastral control point based on the WGRS. The cadastral control network for CRP is composed of national reference point and cadastral control point. A national reference point is re-classified as CORS and MCP (Multi-purposed Control Point). It is judged that the cadastral control point firstly organizes the 1st grade network based on re-estimated reference point, and then, it is necessary for cooperation plan with the cadastral control points which are newly installed for the introduction of WGRS by a local autonomous entity. To do this, the present investigation estimates some factors such as the present state of reference point, installation history, positioning accuracy, and utilization with regard to current-operating CORS, MCP and re-estimated reference point (RRP). Finally, this investigation proposes the construction of a cadastral control network based on the WGRS for promoting CRP well-matched to the Korean topography.
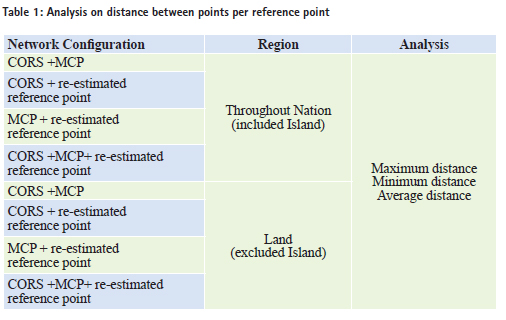
Research contents and methodologyThe main contents and methods of this investigation are as follows; firstly, the current statue of the CORS and reference point with regard to national reference point is analyzed. Secondly, the formation of cadastral control point, previous maintenance history and characteristics, utilization, and the correlation of national reference point, performance differences are analyzed for the connection with cadastral criteria. Thirdly, the linkage with national reference point is established for the efficient use of the construction of cadastral control network based on the WGRS. On the basis of previous estimation, the distribution density of reference point analyzed for CRP; contribute to systemize the construction of cadastral control network and utilization based on WGRS. New strategies for construction of cadastral control networkNational reference point and associated procedures Currently, MOLIT has announced new government guidelines that cadastral confirmation survey should comply with the act of Surveying, Hydrographic Survey and Cadastre in terms of conducting cadastral survey based on WGRS. At the same time, due to the social disarray induced by the transformation of WGRS, the exception regarding the postponement is made until 31 December 2020. The cadastral control point based on the WGRS for CRP should be organized around the CORS, MCP, re-estimated reference point, instead of connect with previous cadastral control point. Every performance of cadastral survey is generally presented by the point based on the WGRS, it should be connected with national reference point considered as the basic format for the WGRS. In this research, the linkage of national reference network is constituted by correlatively connecting with 56 CORS, 1200 MCP network, and 1600 re-estimated reference network for the construction of cadastral control network based on the WGRS. Density analysis by using distance between points The cadastral control network proposed in this investigation used the CORS and MCP as a criterion among national reference points, and the cadastral control point re-constructed in 2009 is the keypoint of investigation in terms of the construction of reference network. In order to analyze the national placing density of cadastral control network based on the WGRS, it should be inevitably estimated the network configuration and distance between points from CORS, MCP, and the re-estimated reference point. In this investigation, an acceptable accuracy has been computed by error propagation law; this is conducted in accordance with the order of primary consideration. Analysis on distance between points included island First of all, the distance between points located within the triangulation control network which has been constructed by CORS, MCP, and re-estimated reference point included at Jejudo, Ulleungdo, Dokdo, and Baelyeungdo has been analyzed. Figure 2 shows the analysis of distance between these points. The triangulation control network has been formed with the connection of CORS and MCP located throughout Korea. As a result of the analysis of the distance between points within this network, the maximum distance is approximately 430km while the minimum distance is about 0.005km. This investigation is to check the overall distribution of simplex network and distance between points. It is enable to be evaluated as just the geometric value because this is not applying for real surveying project. The average distance is about 14km. Analysis on distance between points excluded island The case of the exception for the reference point located in the main island such as Jejudo, Ulleungdo, Dokdo, and Baelyeungdo, the analysis on the distance between points of simplex network is shown in Figure 3. In the comparison of distance between points from simplex network organized CORS and re-estimated reference point on the main land, the maximum distance is approximately 180km and the minimum distance is around 0.233km. From these, the average distance is calculated by 9.8km.
Establishment of the standards of acceptable accuracy The accuracy of current cadastral surveying The accuracy in cadastral surveying is classified with mainly three factors; the accuracy for primary control point surveying, surveying method and surveying equipment, the accuracy to restore the boundary on a map to ground boundary point, and the accuracy for maintenance of ground boundary point. The accuracy points mentioned above should have the consistency. Numerical analysis to accuracy When conducting on cadastral control point, the accuracy is defined to total station surveying. This is based on lateration, the accuracy to distance should be suitable for ±(5mm+5ppm) regardless of the type of cadastral control point. However, the currently introduced surveying equipment has the higher accuracy than the one announced in regulation. Therefore, accuracy will not be an issue any more unless the artificial error is induced. When analyzing the accuracy of the distance, with the assumption of 2km average distance between cadastral triangulation control point, if the accuracy ±(5mm+5ppm) of the enforcement regulation of cadastral surveying is applied.
If the location of cadastral triangulation control point from CORS is determined with the accuracy by ±1.2cm, the accuracy of this point must have the level of ±3.2cm. Moreover, if in the conjunction with MCP, the accuracy by the level of ±4.4cm can be determined. In the case of cadastral supplementary control point, its accuracy can be considered by ±0.7cm under the same standards. If the location is determined through those connected with CORS, its accuracy is ±3.1cm. And then, in the location determination connected with MCP, the accuracy by level of ±4.5cm can be expected.
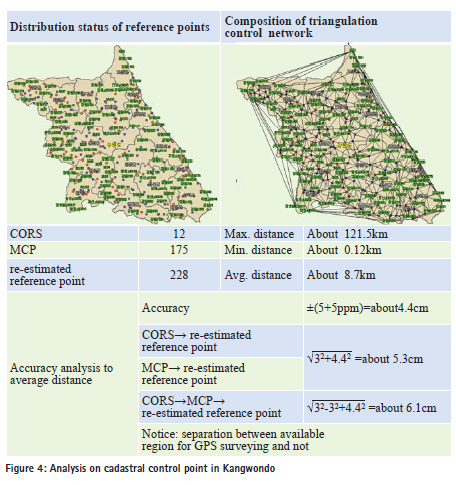
New construction of cadastral control network for CRPEstablishment of the standards The unification between the geodetic and cadastral control point for successfully promoting of CRP in the near future should be firstly carried out adjustment of the unified network. To do this, systematic implementation strategies are required as follows. Analysis on regional reference network (Kangwondo) The worst limitation, in terms of the construction of reference point, is the application of GPS affected on environmental effect. In the particular case of a forest or urban place, the construction of reference point network should be restricted due to the deficiency of the tracking number of the satellite. With the consideration of this viewpoint, the configuration density of reference point and surveying technique are considered depending on the characteristic of topography. The Kangwon province having the highest forest density is performed to the most frequently survey as the combination of GPS and TS. Due to this, it can be expected that this province will carry forward a CRP among the latest target area. Considering the regional features, the average distance between reference points is approximately 8.7km, followed by the Article 9 (Section 1 No.2) of enforcement regulation on cadastral surveying, when using a precise macro meter having a standard deviation of more than ±(5mm+5ppm), the accuracy can be calculated as follows;
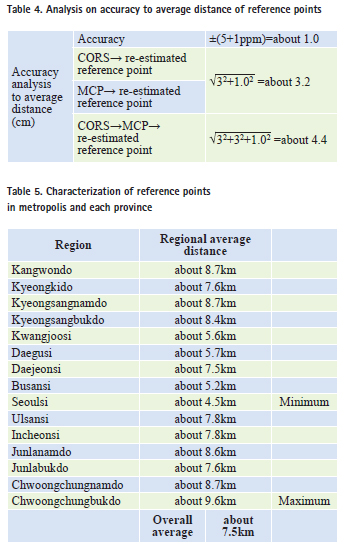
Also, in the case of CORS or MCP, the accuracy is estimated by around 5.3cm. In accordance of the regulation of triangulation surveying the accuracy of the GPS receiver, ±(5mm+1ppm D), the accuracy of GPS receiver itself can be estimated by about 1cm, when measuring from CORS or MCP, the accuracy is about 3.2cm, in the case of the successive measurement of CORS, MCP and re-estimated reference point, the accuracy by 4.4cm is estimated.
New model for reference network The most important factor with regard to construction of new network is the standards for accuracy notified special act on CRP. In the article of this act, in the acceptable range to linkages of performance test, the cadastral control point is ±3cm, and boundary point is ±7cm. According to the estimation of the average distance between points of simplex network organized from regional CORS, MCP, and re-estimated reference point, Seoulsi and 6 metropolitan cities have a shorter average distance than that of other provinces. Even the number of reference point is small compared to the area. The average distance of Seoulsi and 6 metropolitan cities is 6.3km and that of other provinces is 8.5km. Overall average distance is around 7.5km. The distance of the metropolis is longer by 1.2km than overall average distance. When conducting on the measurement of cadastral control point with average distance of 7.5km, the accuracy of theodolite itself is estimated as follow.
In order to meet a acceptable accuracy (±3cm) of special act on cadastral resurvey, it can be implemented by reducing the distance between points with additional installation of reference point. As be calculated this theoretically,
Therefore, the average distance of network which consists of CORS, MCP, and reestimated reference point should be within 5.9km to meet the acceptable accuracy in terms of construction of reference network. In the placing density of current MCP, 1200 reference points is installed through the grid of 10km 10km throughout Korea. Due to the increase of the convenience follow-up surveying, the placing density should be raised by the grid of 5km 5km. However, the installation location of new reference point should be collected by considering on some factors such as geometric strength, the facilities of use, accessibility and convenience of follow-up surveying. The analysis which is calculated in this investigation is just ot theoretical value; the distance between points of new installed point may be changed if regional distribution of reference point and its characteristics are refl ected. However, the result of this investigation is able to utilize as fundamental resources in terms of construction of reference point. The average distance was calculated to 15 different regions. With regard to accuracy from these points, MCP was determined from the performance of CORS, sequentially MCP was applied to determine the reestimated reference point. On all occasions, the accuracy by 7cm is not exceeded. ConclusionFirstly, the simplex network is constructed by linking 72 CORS, 1200 MCP, 1600 re-estimated reference point distributed throughout Korea. As a result of distance between points through simplex network, it can be identified that the average distance included island is about 9km; the average distance excluded island is around 7.7km. The acceptable maximum accuracy is estimated based on ± (5mm+5ppm) accuracy of theodolite surveying. The regional density of reference point should be increased for CRP. Secondly, the distance between points of metropolis and each province is calculated for considering regional characteristics. The average distance of metropolis is 4~5km, however, the case of reference point installed in forest or agriculture region such as Junlanamdo, Kyeongsangnamdo, Kanwondo has the lower density composited by 8~9 km average distance. Since acceptable accuracy is set-up at ±3cm for CRP with consideration on the national average distance of 7.5km, the installation density of reference point should be increased. Thirdly, the average distance of network which consists of CORS, MCP, and reestimated reference point should be within 5.9km to meet the acceptable accuracy in terms of construction of reference network. When considering the convenience of follow-up surveying and installation density of MCP the reference network of 5km 5km is suitable, but to do this, it can be estimated that more than 2000 reference points are necessary. And also, the installation location of new reference points should be collected through the facilities of use, accessibility and convenience of follow-up surveying.
ReferencesAlfred K., P. J. G. Teunissen, 1996, GPS for Geodesy, Springer. Jantien Stoter and Peter van Oosterom, 2003, Cadastral Registration of Real Estate Objects in Three Dimension, URISA Journal . Vol. 15, No. 2. King, R. W. and Bock, Y., 2003, Documentation for the GAMIT GPS Analysis Software, release 10.1, MIT, Cambridge. Mekik, C. and Can, O., 2010, An Investigation on Multipath Errors in Real Time Kinematic GPS Method, J. Sci. Res. And Essays. Tomoji T., 2010, Development of an Open Source Multi-GNSS Data Processing Software, 2nd Asia-Oceania Regional Workshop GNSS 2010. |


















 (7 votes, average: 1.71 out of 5)
(7 votes, average: 1.71 out of 5)




Leave your response!