| GNSS | |
India heads for a regional navigation satellite system
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
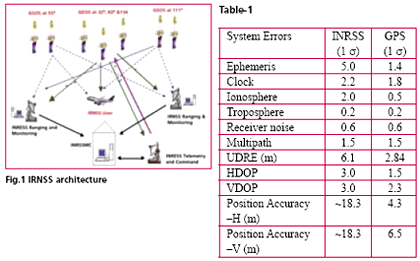
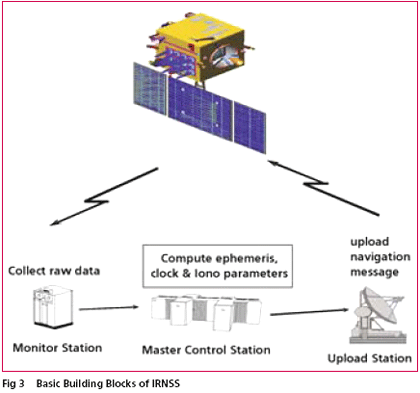
Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has taken up a project called Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS) for the establishment of an independent regional navigational infrastructure. The system main objective is to provide high positional accuracy (comparable to the existing constellations) real time position, velocity and time for various users in the region. IRNSS services will be available on a 24x7x365 basis irrespective of the availability of other constellations over Indian airspace. The system leverages the technological competence of ISRO in satellite, ground and other critical technologies Proposed IRNSS ArchitectureThe proposed architecture of the INRSS consists of space segment, ground segment and user segment. The space segment consists of three GEOs located at 34° E, 83° E and 132° E and four GSOs. The 4 N-GSOS will be placed in the orbit at an inclination angle of 29° with longitude crossing at 55° and 111° East. The ground segment consists of INRSS ranging and integrity monitoring which will be located at 20 places and most of them will be located in the airports along with GAGAN ground elements. IRNSS will have the two Master Control Stations (MCS), which may be co-located with GAGAN INMCC. The proposed INRSS architecture is shown in Fig. 1. The intended coverage area for IRNSS has been proposed to be over the Indian subcontinent and service area will be primarily on the Indian land mass and adjoining areas. The service area for IRNSS is specified as between longitude 40oE to 140o E and between latitude ± 40o. More specifically the coverage should include the Indian subcontinent plus about 1500 Km beyond the Indian geographical area. IRNSS system provides dual frequency (S & L5 band) usage with a targeted position accuracy of less than 10 meters within India. At present one down link in S-band and three down links in L5 band are planned. The system can be augmented with local area augmentation for higher accuracy. The error budget of the proposed IRNSS is given below in Table 1. The proposed IRNSS will be designed indigenously and launched from Indian soil through Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV). The proposed satellite specifications are given below. The snap shot of IRNSS GEOS & GSOS satellite locations are shown in Fig. 2. IRNSS payloadIt will provide signal generation on board and there will be two downlinks providing dual frequency operation with EIRP of 31.5 dBW at EOC. INRSS payload will have 3 Rubidium clocks and Navigation data up link will be through telemetry command link. The payload beam of GSOS will be steered to take care of the inclination. IRNSS Ground Segment FunctionalityThe ground segment consists of MCC, INRSS Ranging and Integrity Monitoring (IRIM) Stations and IRNSS telemetry and command stations. The function of MCC is to estimate and predicts the ephemeris; calculate corrections for SV clock & maintain IRNSS time, Ionospheric corrections and Integrity. The function of IRNSS IRIM stations will be receiving the data from the GEOs and GSOs, transmit the data to MCC and one way ranging of the GEOs & GSOs in S band. The function of IRNSS telemetry and command stations will be to receive telemetry from the IRNSS constellation, Telecomm and the IRNSS constellation and navigation updates. USER SegmentThe user segment will consist of a specially designed inter operable dual frequency receiver, which may receive the data from other constellation of navigation satellite. User segment receiver may be called as multi constellation receiver. The user receiver to get the required position accuracy will continuously track all the seven satellites of INRSS. The user receiver will have minimum G/T of -25 dB/K similar to GPS. ConclusionThe INRSS is under planning stage and ISRO is the main agency to design and implement the entire infrastructure required for operation of the system. It has also to do certification and validation of the signal will be before declaring operational for the users. |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|















 (2 votes, average: 3.50 out of 5)
(2 votes, average: 3.50 out of 5)



