| GNSS | |
System time synchronization for GNSS interoperability
To make it possible for users to solve navigation problem by signals from SVs of different GNSS constellations it is necessary to provide users with data on the offsets between System Time Scales of these GNSS |
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
|
Operational and emerging Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) GPS, GLONASS, Galileo and others provide high-accuracy determination of position, velocity and time for land, marine, airborne and other kinds of users. To achieve this time scales of all Space Vehicles (SV) are synchronized to System Time and System Time is synchronized to Reference Time. National realizations of coordinated time scale UTC are typically used as Reference Time Scales.
Therefore, to make it possible for users to solve navigation problem by signals from SVs of different GNSS constellations it is necessary to provide users with data on the offsets between System Time Scales of these GNSS.
Users can get the data on the offsets autonomously by processing navigation signals themselves from SVs of different GNSS constellations. However, autonomous calculating data on the offsets between System Time Scales of different GNSS constellations is possible only when signals from no less than four SVs of the same GNSS constellation can be received. As a result, it is impossible to use signals from SVs of different GNSS constellations in challenging environment with three or even less visible SVs. Possible solution is to store the calculated values of GNSS-GNSS Time offset and to use the stored values, however this approach brings additional error because of the growing error of the stored values.
Therefore, to provide interoperability with other GNSS in terms of System Time Scales the following procedures are implemented in each GNSS:
– System Time Scale is synchronized to national realization of UTC;
– corrections for the offset between System Time Scale and national realization of UTC are broadcast;- corrections for GNSS – GNSS Time Offset (GGTO) are broadcast.
GLONASS Time generation
GLONASS Time is generated as a continuous “paper” time scale on the basis of the Main or Reserved Central Synchronizers (CS) time scale in accordance with the following equation:
![]()
where – GLONASS Time offset relative to Reference Time; , – Main/Reserved CS time offset relative to Reference Time; , – corrections for Main/Reserved CS phase steering; , – corrections for Main/Reserved CS frequency steering; – correction for controlling GLONASS Time – Reference Time offset; – offset between Main and Reserved CS time scales.
The Central Synchronizer that provides the best accuracy characteristics is used as Master CS, the other operates as secondary.
Central Synchronizers provide the following accuracy characteristics:
– relative frequency error Δf/f below 3·10-14;
– daily frequency instability below 2·10-15.
The backbone of CS is Frequency/Time Keeping Facility (FTKF) including four active Hydrogen Frequency Standards (HFS), a system for internal comparisons and a system for steering frequencies and phases of signals from HFS. HFS which provides the best accuracy characteristics on the results of internal comparisons becomes master standard, the others operate as secondary.
National Time Scale of Russia UTC(SU) generated by State Time/ Frequency Reference (STFR) is used as GLONASS Reference Time.
CS time scale is corrected simultaneously with the correction of coordinated time scale UTC and, as a result, there is no whole second time offset between GLONASS Time and UTC(SU). However, there is a three-hour constant offset between GLONASS Time and UTC due to GLONASS Monitoring and Control Segment operational principles.
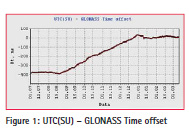
Till August 2014 the offset of GLONASS Time relative to UTC(SU) was about 400 ns. It met specified requirements but was not satisfactory for time users. Therefore, to minimize the offset of GLONASS Time relative to UTC(SU) on 18th August, 2014 the procedure for GLONASS Time correction was started. To keep the specified accuracy of SV – GLONASS Time synchronization the value of daily correction change was 3 ns. The results of monitoring proved the efficiency of the correction procedure: GLONASS Time offset relative to UTC(SU) changed from -392.6 ns (19.08.2014) to 29.4 ns (31.12.2014). Now the offset is kept within 35 ns. The offset of GLONASS Time relative to UTC(SU) is presented in Figure 1.
GLONASS Time broadcast to users
To provide users with navigation and timing data GLONASS SVs broadcast in their navigation messages frequency/ time corrections (FTC) for SV time scale offset relative to GLONASS Time.
To calculate FTC for SV time scale offset relative to GLONASS Time it is provided:
– the offset of SV time scale relative to Measuring Systems (MS) time scale is calculated and the results obtained are used to calculate the offset of SV time scale relative to GLONASS Time;
– the values of the offsets obtained for specified observation time interval are processed together to estimate and predict the parameters of SV time scale offset trend for specified time interval;
– FTCs to be uploaded are generated in a specified part of navigation frame.
The offset of SV time scale relative to MS time scale is calculated with using simultaneous one-way range measurements by One-Way Measuring Systems (OMS) and two-way range measurements by Two- Way Measuring Systems (TMS) (one-way/ two-way technique) and by one-way range measurements by OMS and calculated range values (one-way technique).
The values of SV time scale offset relative to MS time scale are converted to the values of SV time scale offset relative to GLONASS Time by consecutive using the parameters of each MS time scale offset relative to Master (connected to Master CS) MS time scale, Master MS time scale offset relative to Master CS time scale and Master CS time scale offset relative to GLONASS Time at session measurement time.
Parameters of SV time scale drift relative to GLONASS Time are estimated with using time scales offset processing algorithm for session results based on linear model and Least Mean Squares (LMS) technique.
Data on FTC is calculated and then uploaded at each SV orbit circle. FTCs are broadcast in SV navigation signals as two linear coefficients of SV – GLONASS Time offset model and for the middle of each 30-minute segment of prediction interval.
GLONASS Time is determined by users in accordance with the following equation:
![]()
where t – onboard satellite time.
In case all GLONASS facilities are in Full Operational Capability mode the error of FTC calculation and generation is about (3.0 – 6.0) ns (rms).
GLONASS Time corrections
To convert from GLONASS Time to UTC(SU) SVs broadcast correction for GLONASS Time offset relative to UTC(SU) in navigation signals.
To generate data on GLONASS Time offset relative to UTC(SU) it is provided:
– the offset of CS time scale relative to STFR time scale is calculated and the results obtained are converted to the offset of GLONASS Time relative to UTC(SU);
– the values of the offsets obtained for specified observation time interval are processed together to estimate and predict the parameters of GLONASS Time drift for specified time interval;
– corrections for GLONASS Time offset relative to UTC(SU) are generated for the navigation frame to be uploaded.
The offset of CS time scale relative to STFR time scale is calculated on the base of their mutual comparisons by the signals from SVs of GLONASS and GPS in differential mode with using “all-in-view” method according to the following equation:

Now the error of calculating Main CS – STFR time scale offset is about 8 ns (rms), Reserve CS – STFR time offset is 13 ns (rms).
Parameters of GLONASS Time drift relative to UTC(SU) are estimated with using special algorithm for processing time scales offset based on linear model and LMS technique.
The corrections for GLONASS Time Figure 1: UTC(SU) – GLONASS Time offset offset relative to UTC(SU) are calculated and uploaded once per day. They are broadcast to users in navigation messages for the middle of each 30-minute segment of prediction interval.
UTC(SU) time is determined by users in accordance with the following equation:
![]()
Till 18th August, 2014 the error of broadcast corrections for GLONASS Time – UTC(SU) offset contained a systematic component of approximately 200 ns. Therefore, on 18th August, 2014 the generated corrections to GLONASS Time were also changed. Now the error of broadcast corrections for GLONASS Time – UTC(SU) offset does not exceed 10 ns (rms). UTC(SU) broadcast by GLONASS is presented in Figure 2.
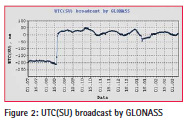
Thus, currently the accuracy of UTC(SU) provided by GLONASS is about 35 ns without using the broadcast corrections to GLONASS Time and about 10 ns with using the corrections.
Corrections for GLONASS – GNSS Time offset
Now GLONASS SVs broadcast GGTO correction only for GLONASS – GPS Time offset , which is the fractional part of GPS – GLONASS Time offset (the integer part is determined by users from GPS navigation message).
To generate data to be uploaded on GLONASS – GPS Time offset it is provided:
– the offset of CS time scale relative to GLONASS Time and GPS Time is measured and the results obtained are used to calculate the values of the offset between GLONASS Time and GPS Time;
– the offsets obtained for specified observation time interval are processed together to estimate and predict the parameters of GLONASS – GPS Time offset drift for specified time interval; – corrections for GLONASS – GPS Time offset are generated to be uploaded in the navigation frame.
The offset between GLONASS Time and GPS Time is calculated with using the measurements at CS in accordance with the equation:
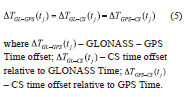
The error of calculating GLONASS – GPS Time offset is about 10 ns (rms). Parameters of GLONASS – GPS Time offset are estimated with using time scale offset processing algorithm based on linear model and LMS technique.
The corrections are calculated and uploaded once per day. They are broadcast to users in navigation messages for the middle of each 30-minute segment of prediction interval.
Now the error of generated corrections for GLONASS – GPS Time offset is below 15 ns (rms). GPS Time is determined by users in accordance with the following equation:
![]()
where – integer part of GPS Time offset relative to GLONASS Time.
Improvement of GLONASS interoperability with other GNSS in terms of System Time
The main approaches to improve GLONASS interoperability with other GNSS in terms of System Time are:
– to increase the accuracy of GLONASS Time synchronization to UTC(SU);
– to increase the accuracy of broadcast corrections for GLONASS Time – UTC(SU) offset;
– to provide users with broadcast GGTO corrections for GLONASS – Galileo Time offset and GLONASS – BeiDou Time offset;
– to increase the accuracy of broadcast GGTO corrections for the offset between GLONASS Time and Time Scales of other GNSS.
These approaches are going to be implemented, first of all, by increasing the accuracy of time scale comparisons between CS time scale and STFR, so it is planned:
– at the 1st stage to install similar calibrated GLONASS/GPS time receivers at STFR and CS. It can provide to determine time scales offset with the error of about 3 ns;
– at the 2nd stage to use time transfer facilities using duplex communication links through satellites in geosynchronous orbit (GEO). It can provide the accuracy of about 1 ns.
Conclusions
Currently, GLONASS interoperability with other GNSS in terms of System Time is provided by the following:
– GLONASS Time is synchronized to UTC(SU) with the accuracy of 35 ns;
– broadcast corrections to GLONASS Time with the accuracy of 10 ns;
– broadcast GGTO corrections for GLONASS – GPS Time offset with the accuracy of 10 ns. As a result of further GLONASS development the following accuracy characteristics are planned to be achieved: – GLONASS Time
– UTC(SU) offset no more than 20 ns at the 1st stage and 4 ns at the 2nd stage; – the error of broadcast corrections to GLONASS Time relative to UTC(SU) below 5 ns at the 1st stage and 2 ns at the 2nd stage; – the error of broadcast corrections for GLONASS – other GNSS Time offset below 3 ns at the 1st stage and 2 ns at the 2nd stage.













 (2 votes, average: 4.00 out of 5)
(2 votes, average: 4.00 out of 5)





Leave your response!