| GNSS | |
Identifying GNSS market in Indonesia before and the future
This paper will highlight the GNSS market in Indonesia before and the future. We found that within ten to fifteen years the GNSS market in Indonesia will be the biggest around South East Asia and probably in Asia Pacific |
 |
|
 |
|
Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) is one of the best finding of the twenty century world technologies. It is satellite base positioning and timing system. A millimeter accuracy of 4D positions can be provided by this GNSS system, allowed us to measure the geodynamic with millimeter per year signal only, measure small deformation and even the change of pole of earth rotation. Not to mention the GNSS for navigation and transportation system, it helps a lot in such traffic management, tracking, controlling, etc. GNSS market has contributed huge amount of dollars in world’s economy. Japan and America are two country of among others for biggest GNSS market so far. As for Indonesia, it is only part of 4% of Asia market in the early 2000. With such similar characteristic between Indonesia and Japan, especially relating to fast growing nation and the ring of fire, in this case market of GNSS in the future can be promising in Indonesia. This paper will highlight the GNSS market in Indonesia before and the future. We found that within ten to fifteen years the GNSS market in Indonesia will be the biggest around South East Asia and probably in Asia Pacific.
Introduction
The revolution in world scale positioning has begun as the satellite technology invented in the beginning of year 70. Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) has been played as remarkable tool for positioning and mapping with high accuracy can be achieved in the easiest way (Seeber [1], Abidin [2-3], Leick [4], Hofmann et. al. [5]). In everywhere and in anytime worldwide when signals from the satellites received by the receivers, in these cases the position in 3D or even 4D can be determined precisely (figure 1) and even with precision in the order of millimeter. Not to mention, the position can be also precisely determined “real-time” in the order of few centimeter by Real Time Kinematik (RTK) Method. The GNSS become a revolution in positioning on the 20th century.
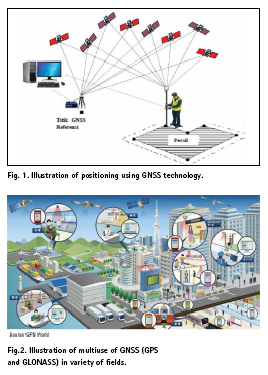
Global Positioning System (GPS) and Globalnaya navigatsionnaya sputnikovaya sistema (GLONASS) are GNSS product by US and Russia. For more than two decade they give all kind of services on positioning and timing. In the case of positioning they allowed us to measure the geodynamic with millimeter per year signal only, measure small deformation and even the change of pole of earth rotation. Not to mentioned their positioning services for survey and mapping and geodetic engineering. In the context of navigation, they helps a lot in such traffic management, tracking, controlling, etc. Figure 2 shows many multiuse of GNSS GPS GLONASS in variety of fields.
In the recent years, the GNSS is expanding when the BEIDOU or COMPAS has been launched by the China, the GALIEO by European Union, QZSS (Quasi Zenith Satellite System) by the Japan, etc. So, today it is not only GPS and GLONASS who existed and give services in positioning and timing, we have more. The additional satellite system is theoretically adding the value to others GNSS System since more satellite can be observed. Also with combination of geostationary and original prograde satellite of 12 hour period, the positioning will be more robust.
With such remarkable services in positioning and timing, GNSS market has contributed huge amount of dollars in world’s economy. Japan and America are two country of among others for biggest GNSS market so far. As for Indonesia, it is only part of 4% of Asia market in the early 2000 (DOC [6]). With such similar characteristic between Indonesia and Japan, especially relating to fast growing nation and the ring of fire, in this case market of GNSS in the future can be promising in Indonesia. This paper will highlight the GNSS market in Indonesia before and the future.
World GNSS market
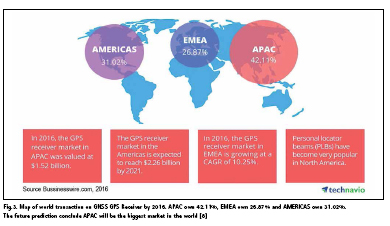
With such tremendous contribution to the world in context of application of positioning and timing (e.g. Navigation, transportation, survey and mapping etc. as mentioned) the GNSS market has given huge amount of dollar in world’s economy like previously mentioned. The value of the world GNSS technology business in 2002 reached $ 9 billion with an annual increase of around $ 1 billion. This means that currently the value of the GNSS technology business is estimated linearly in more than $24 billion. On the other hand an estimation of $ 96 billion is given by GNSS market for present years (GPS World [7]). Global GNSS GPS receiver market by geography shows America and Asia Pacific (but mostly Japan) are the biggest market until today. It is 31.02% and 42.11%. Meanwhile 26.87% credit for Europe and Middle East (Businesswire.com [8]).
In 2016, the GPS receiver market in Asia Pacific (APAC) was valued at $1.52 billion. In the same year the GPS receiver market in Europe and Middle East (EMEA) is growing at a CAGR of 10.25%. The GPS Receiver market in Americas is expected to reach $2.26 billion by 2021 (Businesswire.com [8]).
Do not forget that we just talking about GPS receivers only. As explained above, In the recent years, the GNSS is expanding when the BEIDOU or COMPAS has been launched by the China, the GALIEO by European Union, QZSS (Quasi Zenith Satellite System) by the Japan, etc. Market of receiver is even more huge. Production of Receiver with has BEIDOU channel is growing rapidly. Previously we only familiar with TRIMBLE, LEICA, ASTECH, MAGELLAND and TOPCON, but now we have various brand like SOUTH, HI-TARGET, CHC, NAVCOM, COMNAV, STONEX, HEMISPHERE, UNISTRONG, etc.
Low cost GNSS receiver is also growing quite rapidly, and not to mentioned the handy type like Garmin, Magelland, etc. If we included this segment into economic value, in this case more billions dollar should be added.
China market and economic value of GNSS is still underestimated by calculation. It should be very huge in sales as well as the economic value. GNSS factories are growing rapidly in China. With such big country, the china market of GNSS in their own country will be the same or even bigger than Japan market. We mentioned again that Japan own 44% of world market in the early 2000. GNSS from China is now enter Africa and South America. We can easily found SOUTH Receiver, CHC, HI-TARGET in those continent and sub-continent.

GNSS market in Indonesia
GNSS market in Indonesia is still relatively small. Fields that are using GNSS technology such as navigation and LBS, transportation, survey and mapping and geodynamic study. Indonesia has only 200-300 CGNSS (Continous GNSS) while Japan has more than 1600. First GNSS receiver come to Indonesia was in 1989 and growing market started since 1994. Slowly but sure the market is growing toward positive direction. Roughly note the vendors have sold for more than 5000 geodetic type receiver so far (Geoprima Solution [9], Wisesa Berkah Bumi [10], and Asaba [11]). This is good news for the market.
First let’s talk in detail the beginning the receiver come to Indonesia. It was demo in 1989. After demo the Government realize that GNSS is right tool to help problems of positioning in Indonesia. In 1994 a National Program creating Network Frame for Survey and Mapping executed with GPS. All Benchmark belong to primary and secondary of Network Frame measured by the geodetic type dual frequency receiver. Figure 4 show distribution of Benchmark.
After benchmark being established, another big project being established and indeed even earlier and that is high scale mapping. We used photogrammetry and remote sensing surveys beside conventional tachymetry survey. In order to accomplish the project, help from GPS is crucial. The ground control point for Photogrammetric and High Resolution Satellite Image Data comes from GPS measurements. Fix points of tachymetry is also comes from GPS. In this moment, purchasing of GPS receiver was quite remarkable. Figure 6 shows activities of GPS measurements in the fields.
Since Indonesia is very active tectonically, therefore GPS measurement for geodynamic and deformation is demanding and it started after 2004 Tsunami Earthquake in Aceh. The Government install CGNSS in many places. Approximately we have 200- 300 CGNSS. The receiver put it on the stable benchmark. There are also CGNSS on tide gauge stations, on Buoy, etc. Figure 5 shows tectonic motion of Indonesia. This information is very much useful for earthquake and tsunami mitigation program and also for definition of semi dynamic datum. Today Indonesia has SRGI 2013 semi dynamic datum, replace DGN95 static datum.
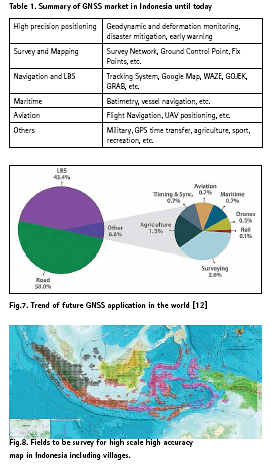
Another market of GNSS is on navigation and LBS using GPS handheld receiver, Integration of GPS with GIS (Geographic Information System) and also with the Smart City. Today the Smart Phone also capable on observing GPS satellite. Now we have many applications that is based on positioning and navigation and or LBS such as Google Map, WAZE, GOJEK, GRAB, UBER, etc. Other LBS (Location Base Services) is also available. Off course those all things adding the value of GNSS economy. Below is table 1 summarize the GNSS market in Indonesia until today.

Future GNSS in Indonesia
Trend of future GNSS applications in the world as well as in Indonesia can be seen in figure 7 below (gsa.europe.eu [13]). Indonesia becomes one of the fastest growing nations and quicker adaptation to the world’s changing. The economic value of GNSS in the market will be tremendous. GNSS is expected to service many more fields in the future than today. The trend will be to LBS, Road and others (Surveying, Drones, Maritime, Aviation, Timing and Synchronization and Agriculture). The highest trend will be LBS. For countries with such disaster like Indonesia, the GNSS application for monitoring and disaster mitigation will also be future trend to accelerate.
With such similar characteristic between Indonesia and Japan, especially related to fast growing nation and the ring of fire, Indonesia will be one of the biggest market around South East Asia and even in Asia Pacific. Indeed the future prediction conclude APAC will be the biggest market in the world while Indonesia is belong to APAC. In another word Indonesia is also belong to the potential market for some reasons.
Indonesia is spatially bigger than Japan. If Indonesia applies GNSS in many fields, it is not impossible to defeat Japan and other countries. As noted earlier, Indonesia is still a 4.7% market share in South East Asia. This means that if Japan has reached 44%, then the deviation value is still very large as an opportunity.
The mandate of the Geospatial Information Act No. 4 of 2011 has opened up opportunities for surveys and mapping to high accuracy, which requires GNSS technology. The Indonesia Geospatial Agency (BIG) as a trustee institution must produce 1: 1000 maps of the entire territory of Indonesia, including the mapping of 80,000 villages (figure 8).
Disaster-laden Indonesia needs GNSS technology for disaster monitoring and mitigation. Indonesia is full of earthquakes, tsunamis, landslides, floods, etc. GNSS technology can be used as a module in modeling disaster phenomena, which in turn becomes an input for disaster mitigation models. Estimation of CGNSS for geodynamic study to be installed in Indonesia is 6000 (base on figuring 1600 at Japan). Not to mentioned for natural deformation purpose.
If we talking man made deformation (e.g. deformation on buildings, bridges, road, railways, platform oil and gas, DAM, etc.), prospect of GNSS to monitor man made deformation is very bright. Huge infrastructures is being developed today in all over Indonesia (figure 9). Today only few programs have been set up to monitor some bridges, platform oil and gas and DAM. Probably no program yet on monitoring building, road and railways. So, we can imagine the prospect in the future.
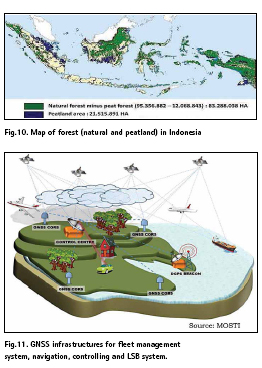
Indonesia is one of the biggest archipelago country in the world. Located in the equator regions Indonesia is rich for natural resources such as forest (figure 10), fishing ground, farmland, mining, etc. Managing all resources need position as one basic parameters. So, we can imagine another prospect in the future for GNSS in Indonesia. One finest example in the future is precise farming. The others are delineation of forest boundary, calculate size of mining area, etc.
Land parcel in Indonesia consist of about 140 millions unit. Until today only 50 million is well define (e.g. certified). The rest we still need measurements. For about couple years ago, the RTK multi GNSS plays an important role in measuring land parcel in Indonesia. This RTK can speed up the measurement (Andreas [14]). Base on record from vendors (Geoprima Solution [9], Wisesa Berkah Bumi [10], and Asaba [11]), GNSS receiver selling reached more than 2000 unit in order to support land parcel measurements. In the future they estimate there will be more millions to sell. Land parcel certification expected to finish by 2025.
As for fleet managements system, navigation, tracking and controlling system, figure 11 show future of them in the world. Indonesia has the same future figure. As mentioned earlier in Indonesia now we have many applications that is based on positioning, navigation and LBS such as Google Map, WAZE, GOJEK, GRAB, UBER, etc.
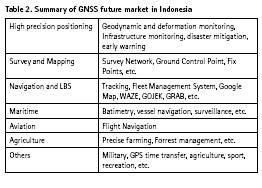
Based on research on literature, interviewed and questionary the Goverment, the Experts, Academia, the Vendors, the variety of users, we found that within ten to fifteen years the GNSS market in Indonesia will be the biggest around South East Asia and probably in Asia Pacific. Below is table 2 summarizing the future GNSS market in Indonesia.
Closing remarks
In everywhere and in anytime worldwide when signals from the GNSS satellites received by the receivers, in these cases the position in 3D or even 4D can be determined precisely and even with precision in the order of millimeter. Not to mention, the position can be also precisely determined “real-time” in the order of few centimeter by Real Time Kinematik (RTK) Method. The GNSS become a revolution in positioning on the 20th century.
For more than two decade the GNSS give all kind of services on positioning and time. In the case of positioning they allowed us to measure the geodynamic with millimeter per year signal only, measure small deformation and even the change of pole of earth rotation. Not to mentioned their positioning services for survey and mapping and geodetic engineering. In the context of navigation, they helps a lot in such traffic management, tracking, controlling, etc.
With such tremendous contribution to the world in context of application of positioning and timing, the GNSS market has given huge amount of dollar in world’s economy. Global GNSS GPS receiver market by geography shows America and Asia Pacific (but mostly Japan) are the biggest market until today. It is 31.02% and 42.11%. Meanwhile 26.87% credit for Europe and Middle East. China market and economic value of GNSS in this country is still underestimated by calculation. It should be very huge in sales and in the economic value. GNSS factories are growing rapidly in China. With such big country, the china market of GNSS in their own country will be the same or even bigger than Japan market.
GNSS market in Indonesia is still relatively small as for today, nevertheless slowly but sure the market is growing toward positive direction. Based on research on literature, interviewed and questioner, we found that within ten to fifteen years the GNSS market in Indonesia will be the biggest around South East Asia and even in Asia Pacific.
Acknowledgements
Many thanks to students and surveyors who help us in distributing the questioner. Thanks also to people (expert, Academia, Government and bussinessman) who willing to interviewed.
References
1. Seeber, G., Satellite Geodesy: foundation, method, and applications, Walter de Gruyter, Berlin-New York, C7 (1993)
2. Abidin, H.Z., Penentuan Posisi dengan GPS dan Aplikasinya (PT. Pradnya Paramita, Jakarta, 1999)
3. Abidin, H.Z., Geodesi Satelit (Departemen Teknik Geodesi ITB, PT. Pradnya Paramita, Jakarta, 2001)
4. Leick A. GPS satellite surveying, 3rd edn Wiley, New York (2004)
5. Hofmann-Wellenhof, B., Lichtenegger, H. and Walse, E., GNSS Global Navigation Satellite Systems: GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, and More. (Springer Verlag, Wien, 2007)
6. DOC, Sales Reporton the GPS Market (2008)
7. GPS World, News Report (2015) 8. Businesswire.com. Internet access May 2018 (2016)
9. Geoprima Solution Ltd. Interview and Questioner 2018 (2018)
10. Wisesa Berkah Bumi Ltd. Interview and Questioner 2018 (2018)
11. Asaba Indonesia Ltd. Interview and Questioner 2018 (2018)
12. BIG (Badan Informasi Geospasial). Presentation on the seminar Establishing New References System for Indonesia (SRGI 2013), Jakarta (2012)
13. Gsa.europe.eu, Internet access May 2018 (2018)
14. Andreas, H., 2017, Percepatan Pemetaan Persil Menggunakan Teknologi Mobile Base Station (MOBS) RTK MULTI GNSS dan RTPPP, Conference Proceeding FIT ISI CGISE Jogjakarta, Indonesia (2016).
The paper was presented at ISGNSS 2018 E3S Web of Conferences 94, 03010 (2019)














 (3 votes, average: 2.67 out of 5)
(3 votes, average: 2.67 out of 5)




Leave your response!